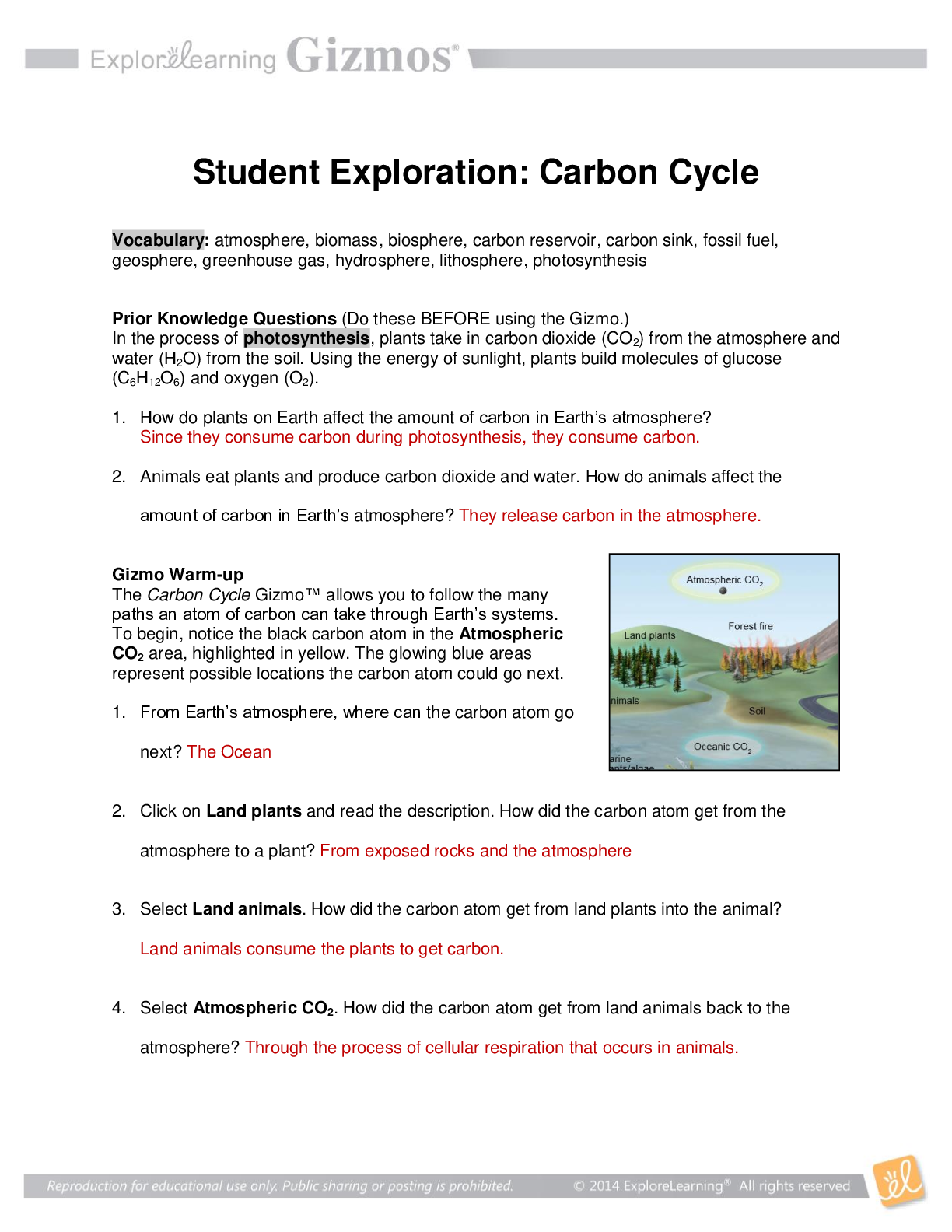
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
1. Why do you think it is important to cover your mouth when you cough?
__It is important to cover your mouth because if you do not cover your mouth
germs c
...
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
1. Why do you think it is important to cover your mouth when you cough?
__It is important to cover your mouth because if you do not cover your mouth
germs could spread______
2. Why should you always wash your hands before you eat? __________________________
__\You should wash your hands before you eat just incase your hands have
germs on them that way you don’t transfer germs to your food and from the
food to your mouth________________
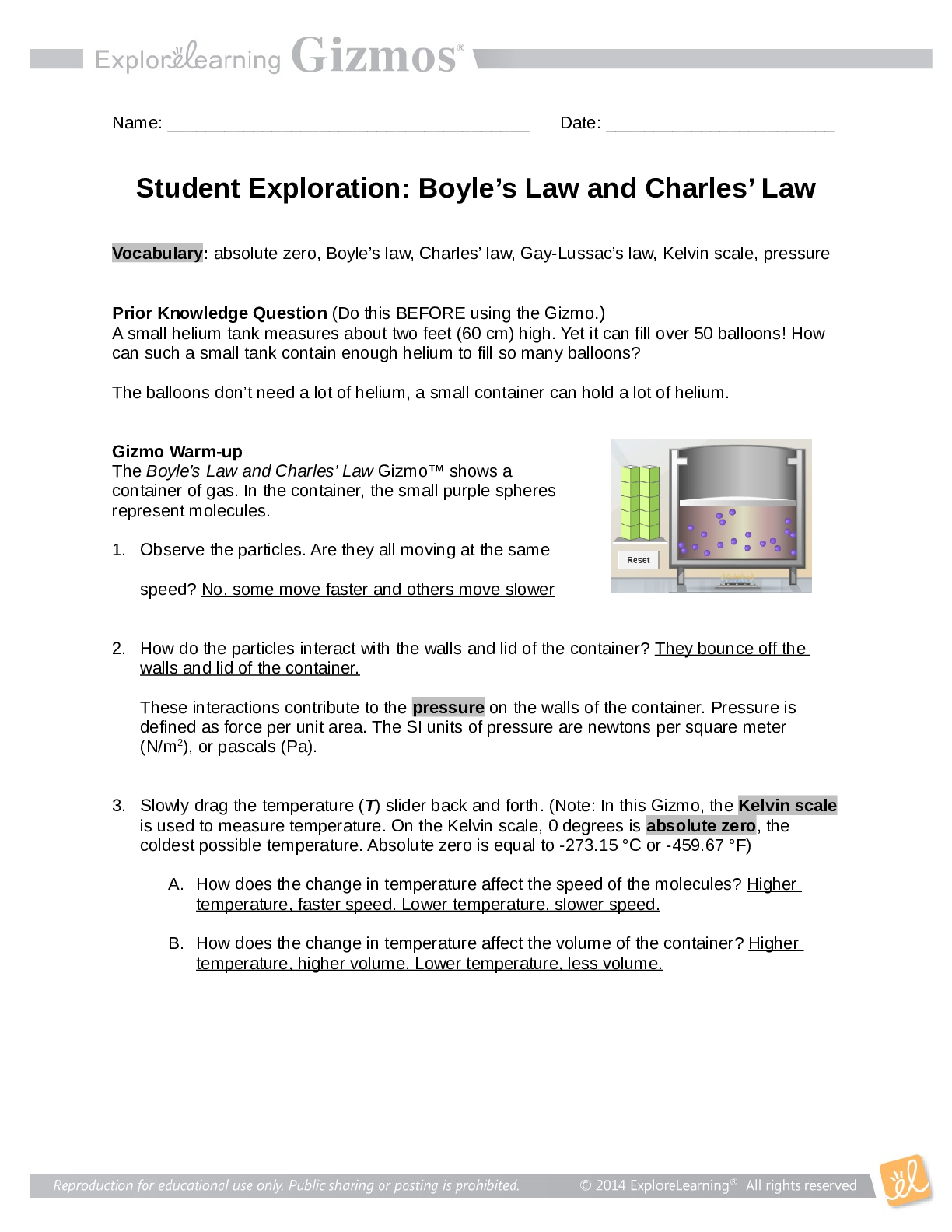
Gizmo Warm-up
When a person has a disease, his or her normal body
functions are disrupted. Some diseases, such as diabetes
and most cancers, are not spread from one person to
another. But other diseases, such as the flu and strep
throat, can be spread. These diseases are known as
infectious diseases. Infectious diseases are caused by
viruses, bacteria, and other agents known as pathogens.
In the Disease Spread Gizmo, you will be able to observe
how various pathogens can spread through a group of
people. Click Play ( ) and observe.
1. Describe what happened on the SIMULATION pane: _______________________________
_As the people move around more people get affected by food_____
2. Look at the color key on the bottom right of the Gizmo. What is happening when a person
changes color?
On the simulation, a person changes color to indicate the person has become infected
with a disease. The color green indicates the person is infected with a foodborne disease
Activity A:
Person-to-person
transmission
Get the Gizmo ready:
● Click Reset ( ).
● On the CONTROLS tab under Active Diseases,
turn off Foodborne and turn on Person to person.
● Set the Number of people to 5.
Question: What factors affect how quickly a pathogen spreads from person to person
This study source was downloaded by 100000796615030 from CourseHero.com on 07-07-2021 06:32:52 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/61376382/Copy-of-Juliette-Baldwin-Disease-Spread-Gizmodocx/
This study resource was
shared via CourseHero.com
1. Predict: Some pathogens are spread directly from one person to another. This can happen
when people come into direct contact or share items, such as drinking glasses. What do you
think might affect how quickly a pathogen is spread from person to person?
Population density and ease of transmission or the two primary factors affecting the
infection rate of a disease
2. Identify: Select the SIMULATION tab on the left and the TABLE tab on the right. (You will
want the table tab open to answer question C.)
A. What does the purple person represent? An infected person
B. Click Play, and observe the simulation for a while. What must happen for the disease
to spread from one person to another? People must come into direct contact
C. How long did it take to infect five people? _15hr_________
3. Experiment: Click Reset. Change the Number of people to 15. Click Play, and record how
long it takes to infect five people. Then repeat the experiment when there are 25 people and
35 people in the room.
Number of people in room Time required to infect five people (hr)
15 5.2hr
25 4.3hr
35 3.0hr
4. Interpret: Study the data you collected. What trend do you see in the data, and how would
you explain it? As the number of people in the room increased, the time required to
infect five people decreased. This most likely occurred because the contact between
people became more common as the room got more crowded, making it easier. For
the pathogen. To spread
5.Experiment: Not all pathogens are equally infectious. Click Reset. Set the Number of people
to 20. Under Probability of transmission, select Low for Person to person.
On the SIMULATION tab, click Play. Record the time it takes to infect five people. Then
repeat the experiment with a medium and high probability of transmission. (Note: For the
“Medium” setting, move the slider half-way between the Low and High positions.)
Probability of Transmission Time required to infect five people (hr)
Low 74.6hr
Medium 5.9hr
High 3.1hr
5. Interpret: Study the data you collected in the table above. What trend do you see in the data,
and how would you explain it?
As the probability of transmission increased the time required to infect five people
decreased is most likely occurred because a higher probability of transmission
made it more likely that the pathogen would spread from one person to the next
6. Analyze: On the CONTROLS tab, place the Probability of transmission slider under
Person to person half-way between Low and High. Select the SIMULATION and GRAPH
tabs. Click Play.
A. At what time did the disease spread most slowly? Most quickly?
It's spread the most slowly in the first few hours but as more people became infected the
rate of transmission increased
This study source was downloaded by 100000796615030 from CourseHero.com on 07-07-2021 06:32:52 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/61376382/Copy-of-Juliette-Baldwin-Disease-Spread-Gizmodocx/
This study resource was
shared via CourseHero.com
B. How could you explain this change in the rate of the disease’s spread?
The disease spreads when infected people meet uninfected people this happens
most frequently when there are equal numbers of infected and uninfected people
the disease spreads more slowly when there are very few infected people or very
few healthy people
Apply: An epidemic is the rapid spread of an infectious disease. How do you think a
government could try to prevent an epidemic of a dangerous person-to-person
pathogen?
The government could be on public gatherings and encourage people to limit their
contact with others
Activity B:
Foodborne and
airborne
transmission
Get the Gizmo ready:
● Click Reset.
● On the CONTROLS tab under Active diseases,
turn off Person to person and turn on Foodborne.
Question: How do foodborne and airborne pathogens spread?
1. Predict: How do you expect the spread of a foodborne disease to be similar to and different
from the spread of a person-to-person disease?
Both types of diseases are transmitted when a person comes in contact with
something carrying a pathogen in a foodborne disease is the pathogen is carried by
food rather than a person
2. Observe: Select the SIMULATION tab. Click Play and closely watch the people moving
around the room.
A. What does each person do just before becoming infected?
They visit the buffet table
B. How are foodborne pathogens transmitted?
By consuming a food/beverage that contains a pathogen
C. If a person in the simulation never eats or drinks anything from the buffet table, is it
possible for them to become sick with the foodborne disease? Explain your answer.
In order to be infected with the food borne disease a person must eat or drink from
the buffet table people are not infected with the foodborne disease in any other way
3. Analyze: Select the GRAPH tab, and wait for every person to become infected.
C. At what time did the disease spread most slowly? Most quickly?
The disease spread most quickly at the beginning and more slowly at the end of
the simulation
D. How could you explain this change in the rate of the disease’s spread?
The more that time passed the more likely it was a person that would visit the buffet table
in the first several hours many people visit at the table the rate of spread decreased as
fewer and fewer people were left who had not visited the buffet table
(Activity B continued on next page)
Activity B (continued from previous page)
4. Compare: How does the spread of a foodborne pathogen compare to the spread of the
person-to-person pathogen you studied in activity A?
The food borne pathogen spread slower because the likelihood of coming in contact with
the pathogen did not increase over time as I did with the person to person disease
5. Predict: How would you expect the spread of an airborne disease to be similar to and
different from the spread of a foodborne disease and a person-to-person disease?
All these diseases are transmitted when the person comes in contact with something
carrying a. pathogen an airborne disease will likely be transmitted faster because it is
more likely for a person to breathe in contaminated air than to come in contact with a
This study source was downloaded by 100000796615030 from CourseHero.com on 07-07-2021 06:32:52 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/61376382/Copy-of-Juliette-Baldwin-Disease-Spread-Gizmodocx/
This study resource was
shared via CourseHero.com
pathogen carrying person or food item
6. Experiment: Run a few simulations with the airborne pathogen.
A. What patterns do you notice in how the airborne pathogen spreads?
The pathogen seems to spread randomly
B.How does the spread of an airborne pathogen compare to the spread of foodborne
and person-to-person pathogens?
The person does not need to come in contact with another person or food item to
become infected simply being in the room can lead to infection
7. Think about it: Suppose there is an infectious disease at a party. How could doctors tell if the
disease was foodborne, airborne, or transmitted person to person?
Doctors could study the rate of disease transmission and interview patients and
determine where they have been and with who or what they have come in contact with
before falling ill if everybody who is certain food became ill doctors would likely suspect
a foodborne illness if a group of people who all came close in contact at the party
became ill doctors would likely suspect a person to person to see if people became ill
randomly doctors might suspect an airborne disease
This study source was downloaded by 100000796615030 from CourseHero.com on 07-07-2021 06:32:52 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/61376382/Copy-of-Juliette-Baldwin-Disease-Spread-Gizmodocx/
This study resource was
[Show More]





















.png)