EXAMPLE 1
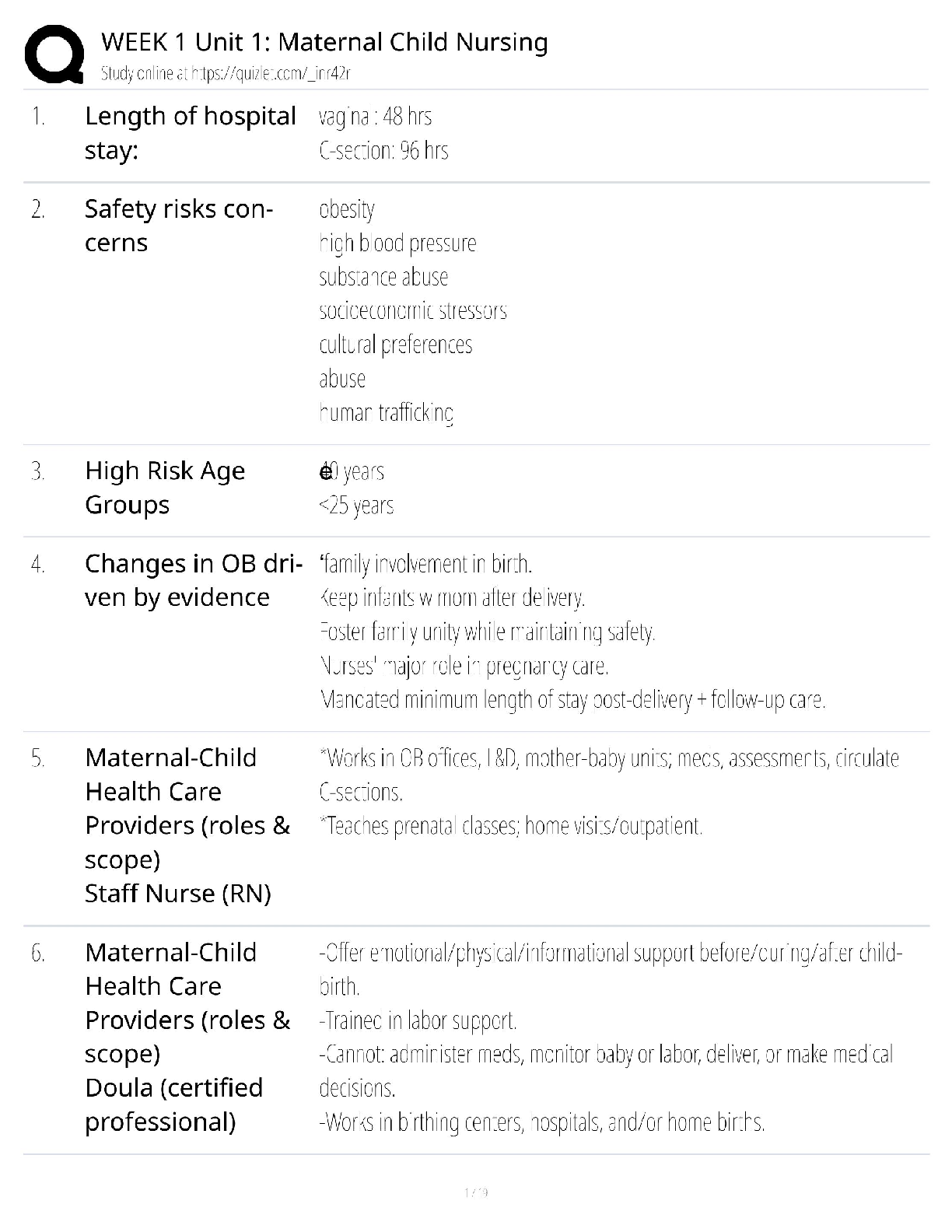
At any instant the horizontal position of the weather balloon in
Fig. a is defined by where t is in seconds. If the
equation of the path is determine the magnitude and
direction of the velocity and the acce
...
EXAMPLE 1
At any instant the horizontal position of the weather balloon in
Fig. a is defined by where t is in seconds. If the
equation of the path is determine the magnitude and
direction of the velocity and the acceleration when
SOLUTION
Velocity. The velocity component in the x direction is
To find the relationship between the velocity components we will use
the chain rule of calculus.
vx = x
# = d
dt 18t2 = 8 ft>s :
t = 2 s.
y = x2
>10,
x = 18t2 ft,
vy = y
# = d
dt 1x2
>102 = 2xx#
>10 = 21162182>10 = 25.6 ft>s c
When the magnitude of velocity is therefore
Ans.
The direction is tangent to the path, Fig.b, where
Ans.
Acceleration. The relationship between the acceleration components
is determined using the chain rule. We have
Thus,
Ans.
The direction of a, as shown in Fig.c, is
Ans.
NOTE: It is also possible to obtain and by first expressing
y = f1t2 = 18t2 and then taking successive time derivatives. 2
>10 = 6.4t
2
vy ay
ua = tan-1 12.8
0 = 90°
a = 4(02 2 + (12.822 = 12.8 ft>s
2
= 21822
>10 + 21162102>10 = 12.8 ft>s
2 c
ay = v
#
y = d
dt 12xx#
>102 = 21x
#
2x
#
>10 + 2x1x
$
2>10
ax = v
#
x = d
dt 182 = 0
uv = tan-1
vy
vx
= tan-1 25.6
8 = 72.6°
v = 4(8 ft>s22 + (25.6 ft>s22 = 26.8 ft>s
t = 2 s,
y
A
B
x
16 ft
(a)
y x2
10
(b)
B
v 26.8 ft/s
uv 72.6�
(c)
a 12.8 ft/s
2
B
ua 90�
EXAMPLE 2
For a short time, the path of the plane in Fig. a is described by
If the plane is rising with a constant velocity of 10 ,
determine the magnitudes of the velocity and acceleration of the plane
when it is at
SOLUTION
When , then or . Also, since
, then
;
Velocity. Using the chain rule to find the
relationship between the velocity components, we have
(1)
Thus
The magnitude of the velocity is therefore
Ans.
Acceleration. Using the chain rule, the time derivative of Eq. (1)
gives the relation between the acceleration components.
When
The magnitude of the plane’s acceleration is therefore
Ans.
These results are shown in Fig.b.
[Show More]