
CLC 013 Performance Based Services Acquisition BEST STUDY MATERIAL WITH FULL INFORMATION
$ 15

Colostomy Care Plan
$ 5

NUR 112 Learning Objectives Final Exam
$ 9.5

Essentials of Nursing Research appraising evidence for nursing practice 9th edition Denise Pilot
$ 15

Midterm Exam 2 Questions & Answers (Verified Answers), 100% Guaranteed Pass ||Complete A+ Guide
$ 20

WGU C961 - Ethics in Technology Questions and Answers Graded A+
$ 8
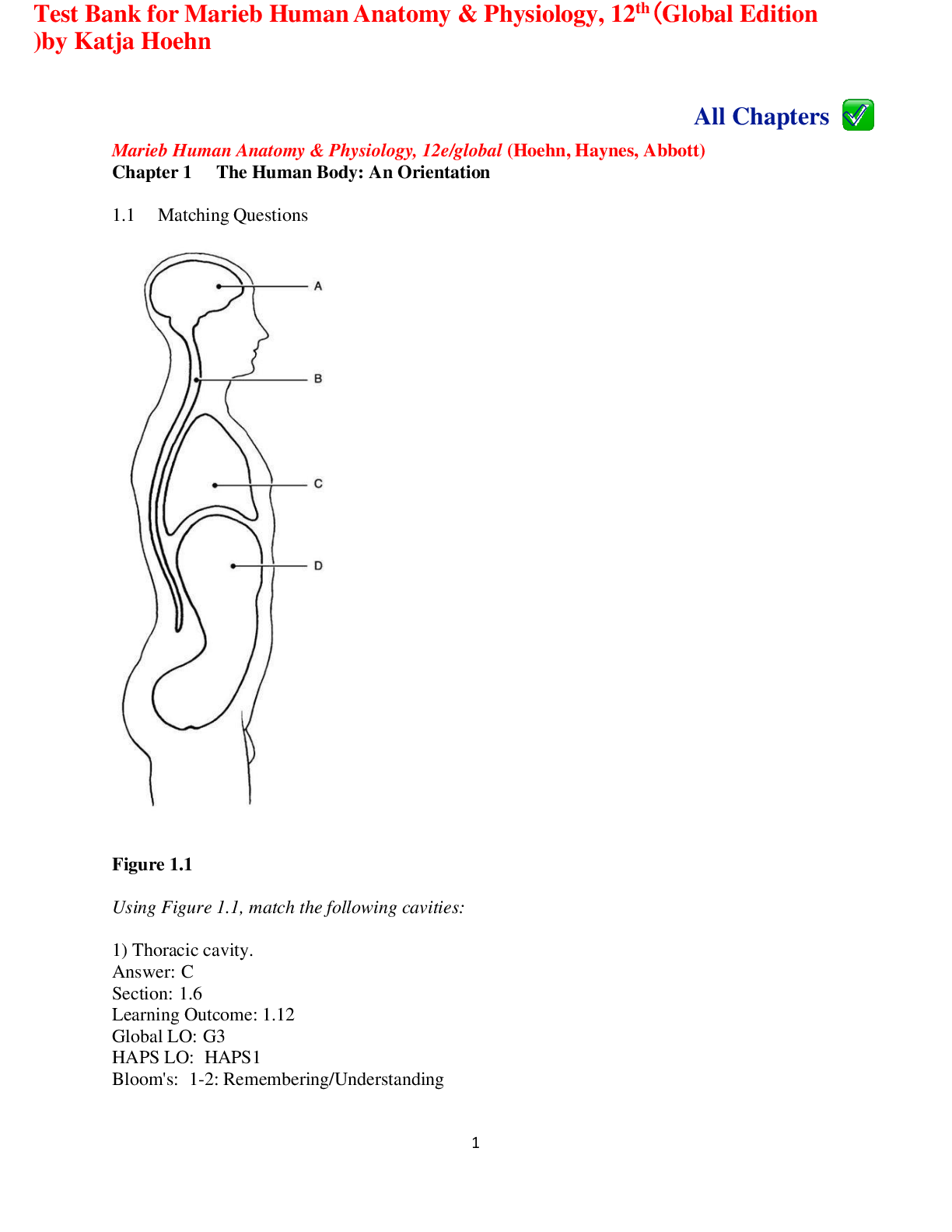
Test Bank for Marieb Human Anatomy & Physiology, 12th(Global Edition )by Katja Hoehn
$ 20

PDF (eBook) Radicalisation, Extremism and Social Work Practice, Lena Robinson ,M Rafik Gardee,1e
$ 25

ARDMS Review Sonography basics 62 Questions with Verified Answers,100% CORRECT
$ 8.5

Stockholders'Equity. Best Study Notes
$ 4.5

UMUC IFSM 201 Excel Project 2 IFSM 201 7394 Concepts and Applications of Information Technology
$ 14.5

eBook [PDF] The Decision Intelligence Handbook Practical Steps for Evidence-Based Decisions in a Complex World 1st Edition By L. Y. Pratt, N. E. Malcolm
$ 29
.png)
CHEN 3010 – Reaction Engineering Lab-1 Report Experiment 6 – Armfields catalytic reactor (Exercise A)
$ 12

HESI_A2_Math_Study_Guide | Lamar University | Download To Score An A
$ 24

Chapter 43: Hematologic and Immunologic Dysfunction Nursing School Test Banks
$ 20

Psychotherapy for the Advanced Practice Psychiatric Nurse, Second Edition: A How-To Guide for EvidenceBased Practice 2nd Edition Test Bank
$ 15.5

SCI 228 Week 6 Quiz (version 2) – 100 % Correct Answers
$ 12

OCR GCSE Media Studies PAPER 1 J200/01: Television and promoting media Mark Scheme for June 2024
$ 8

VATI ATI GREENLIGHT PREDICTOR Version Newest 2025 WITH Complete Questions And Correct Detailed Answers (Verified Answers)|Already Graded A+||BRAND NEW!!
$ 15.5

HIST 405N Week 1 Case Study Assignment Option 1: Exploration and Effects on Native Americans

















 (1).png)





