
HESI Medical_Surgical LPN -EXAM PACK BEST FOR 2022 EXAM
$ 19
 ans.png)
Final Exam Review (Ch. 9 – 12) KEY
$ 9

NU 635 CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION REVIEW EXAM Q & A 2024 HERZING
$ 10

Discussion answers on computer fraud. Download for higher grades.
$ 10

OCR A Level in Design and Technology: Product Design H406/01 Principles of Product Design MARK SCHEME - October 2021
$ 4.5

ADVANCED Med SURG HESI Final RN V2 TEST BANK
$ 30

WGU - D313 - Anatomy And Physiology 2 Lymphatic System Practice Test (Latest 2026 / 2027) Questions & Answers with Rationale | Grade A
$ 15

A Level Physics A H556/02 Exploring physics June 2023 QP
$ 4

Rich AF: The Winning Money Mindset That Will Change Your Life Kindle Edition by Vivian Tu
$ 4.5

Pearson Edexcel_International GCSE (9–1) Physics_4PH/1PR Question Paper Jan 2021 | Paper: 1PR
$ 7.5

(WGU D379) MKTG 6020 Social Media Health Care Marketing Objective Assessment Guide Q & A 2024
$ 12

ADM 201 - Salesforce Certification What is affected by changing the default locale set
$ 10

STAT Broward College 2023
$ 14

Georgia Institute Of Technology - CS 7638kalman_Filter2D.py
$ 6
.png)
NRS-440V Topic 2 – Discussion Question 1/FULL STUDY/RATED A
$ 14.5

MATH-114 Week 6 Discussion ;Solving Equations using Square Roots or the Quadratic Formula
$ 10

Quality Management for Organizational Excellence:Introduction to Total Quality David L. Goetsch Stanley Davis Seventh Edition
$ 20
SCI 101-Gizmos - Orbital Motion – Kepler’s Laws-answer key-2022
$ 9.5

OCR A Level GCE Chemistry B H433/03 Practical skills in chemistry for June 2023
$ 11.5

(WGU D470) BUS 3900 Transportation, Logistics, and Distribution Objective Assessment Guide Q & A 2024
$ 10

eBook [PDF] Psychopathology A Competency Based Assessment Model for Social Workers 4th Edition By Susan W. Gray_ Marilyn R. Zide
$ 28

Test Bank & Instructor Manual for Stats Modeling the World, 6th edition By Richard D. De Veaux, Paul F. Velleman, David E. Bock
$ 25
.png)
NRS-440V Topic 1 – Discussion Question 2:/FULL STUDY/RATED A
$ 11.5

NR 503 Week 2 Assignment: Healthy People 2020 Impact Paper/ Download To Score An A
$ 20
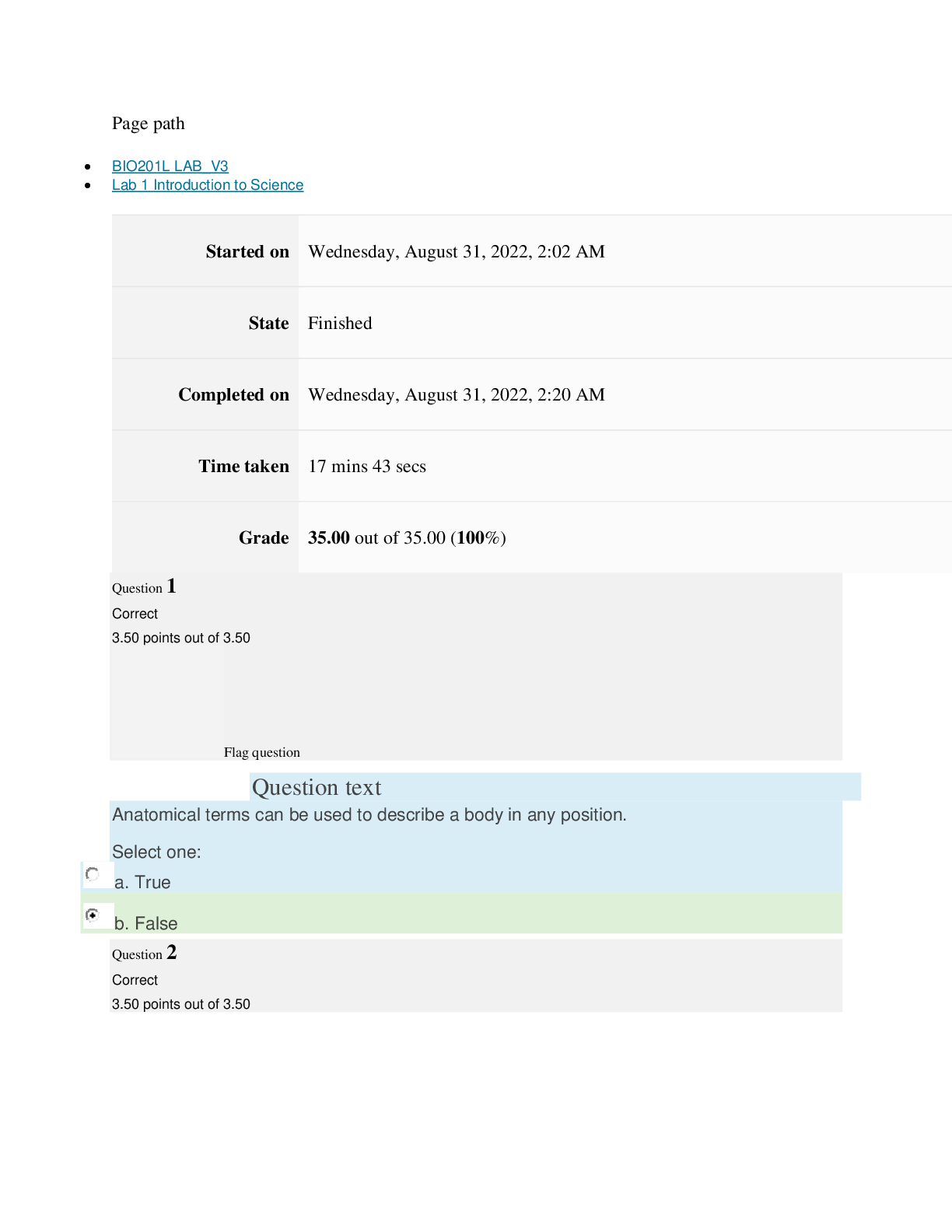
BIO201 LAB 1 INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE[ ALL ANSWERS 100% CORRECT]
$ 4
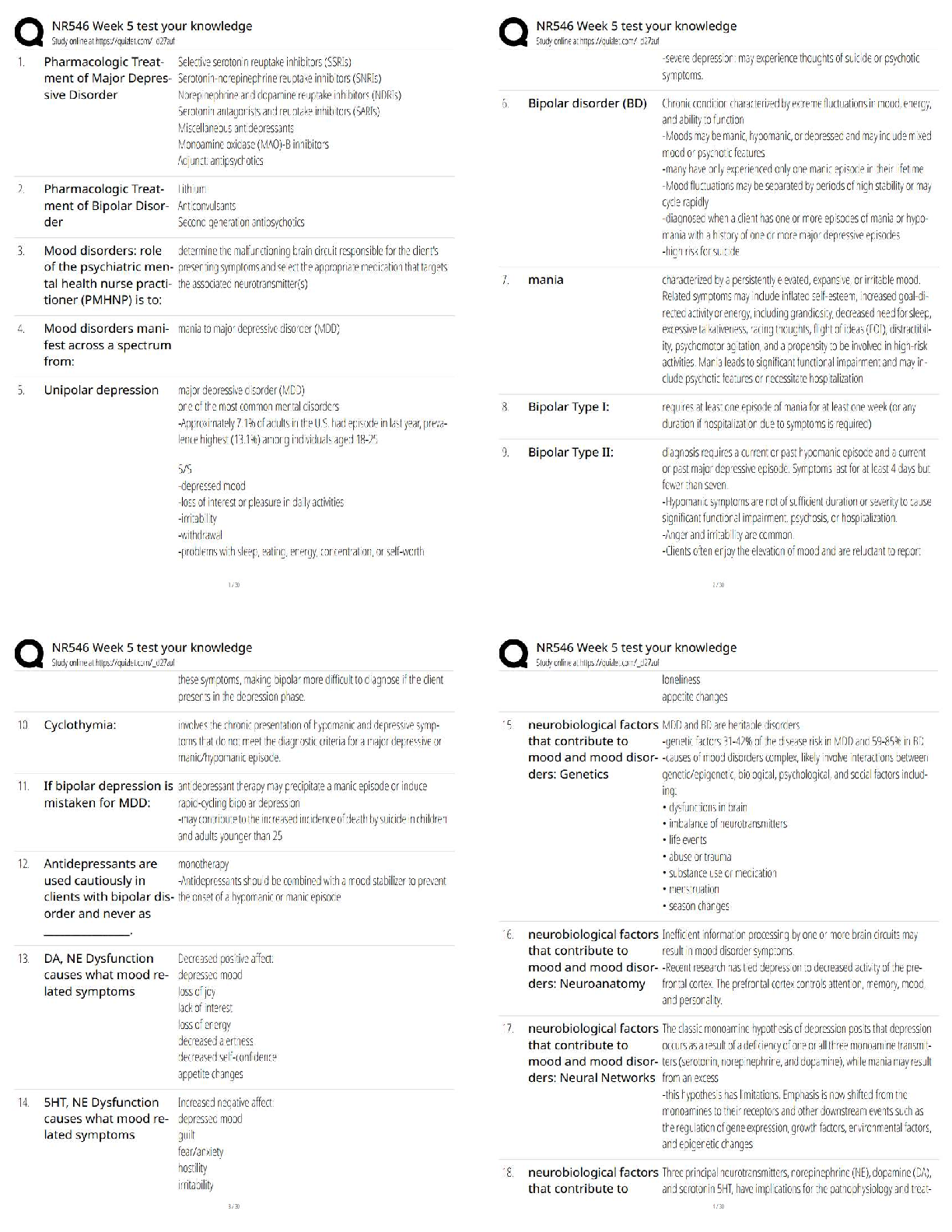
NR546 Week 5 Test Your Knowledge | Psychopharmacology Quiz / Score 100% / 2025 Update
$ 11.5
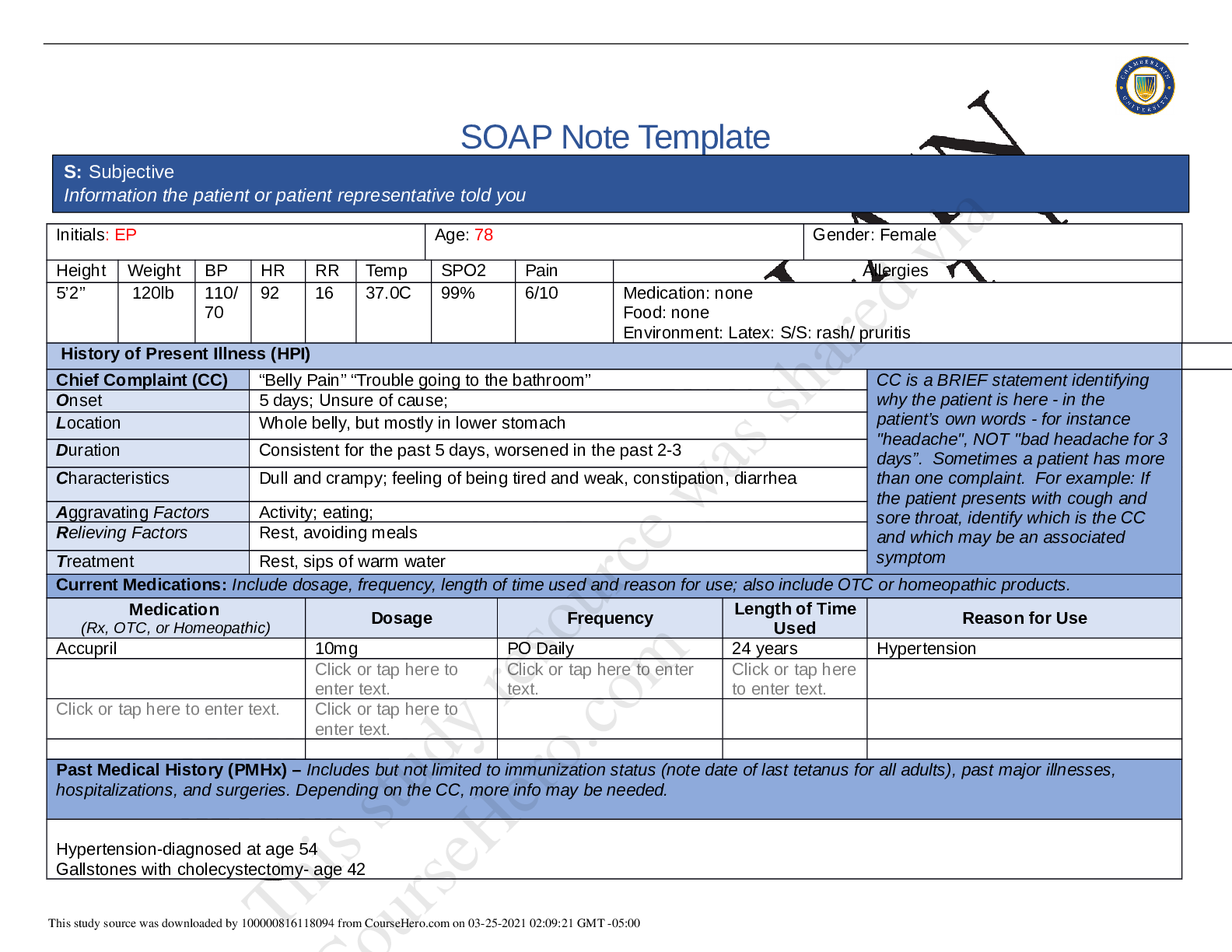
Summary NR 509 Week 5 Abdominal Pain SOAP Note
$ 12

Reference Solution for ms-700.vce MS-700 Managing Microsoft Teams Version 3.0. Score: 800/1000.
$ 14

NUR 243 CLINICAL JUDGEMENT REVIEW EXAM Q & A 2024 HONDROS
$ 13

HESI A&P Test Bank HESI A2 Anatomy and Physiology, HESI A2 Science, HESI A2 Grammar, HESI A2 Math’s, HESI A2 critical thinking, Latest 2022, A++ Guide.
$ 8

University Of Arizona - MIS 111 Computers and Internetworked Society: Exam_2_answer_key
$ 10
PN Final Study Guide/PN Final Study Guide.2020/2021
$ 20

Sitecore 9.0 certification objective exam Questions and Answers
$ 7.5

N4455 Nursing Leadership and Management Module 2 Assignment 1: Organizational Analysis – Shadowing Plan
$ 8

Wong’s Nursing Care of Infants and Children, 12th Edition – Test Bank (Marilyn J. Hockenberry) | Full Pack Solutions | Updated 2025/2026 Instant Download
$ 13.5

William Fredericks iHuman Full
$ 16

PN3 Exam 1 Questions And Answers Latest Version Update
$ 20

eBook [PDF] Teaching Humanity An Alternative Introduction to Islam 1st Edition By Vernon James Schubel
$ 29

[eBook] [PDF] Introduction to the Practice of Statistics, 10th Edition by David Moore, George McCabe, Bruce Craig
$ 32.5
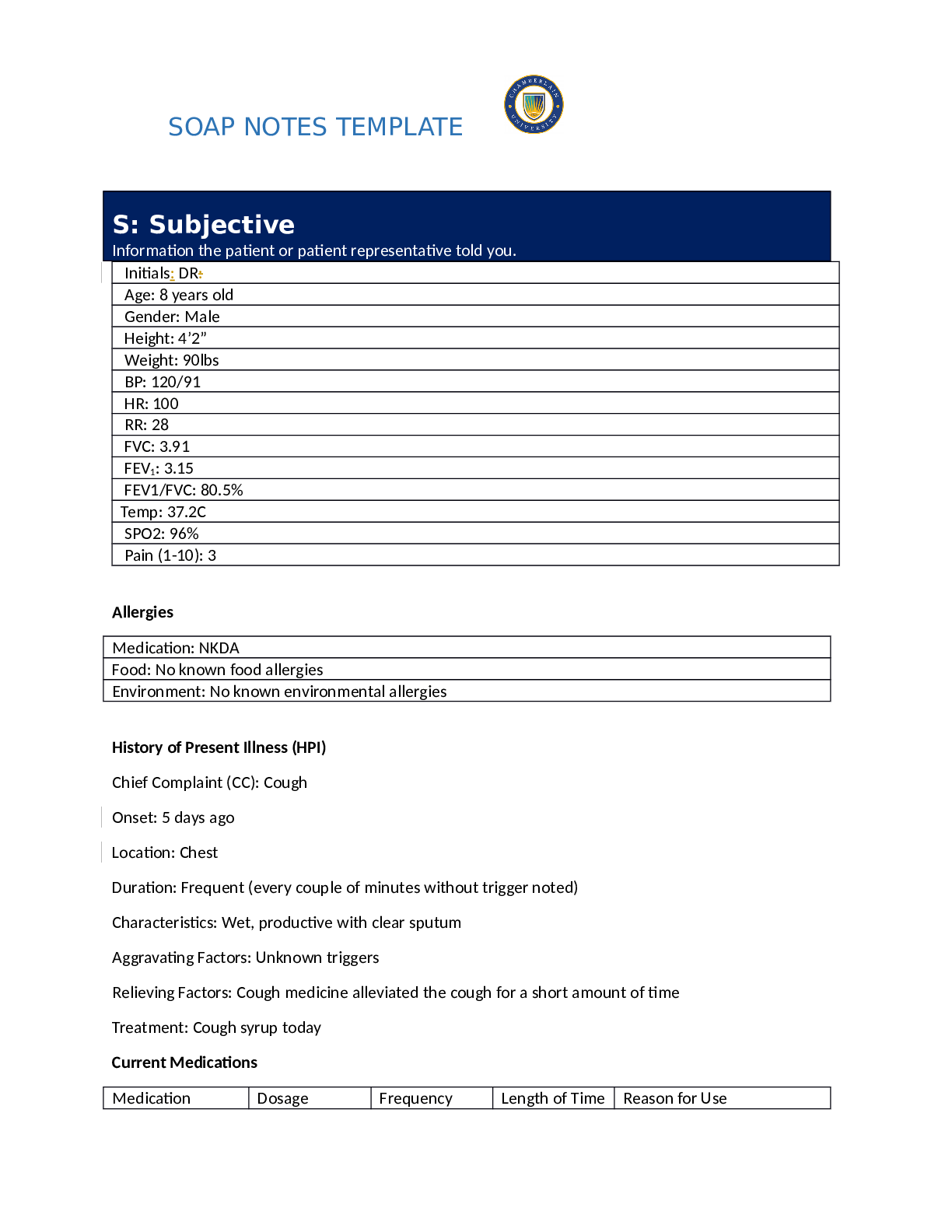
NR 509 Week 6 Pediatric SOAP Note LATEST
$ 15

SCIENCE ProgrammingToWin by Izzy Narvaez
$ 10

PSY 205 LIFESPAN DEVELOPMENT REVIEW EXAM Q & A 2024 HONDROS
$ 16

eBook [PDF] When Music Takes Over in Film 1st Edition By Anna K. Windisch, Claus Tieber, Phil Powrie
$ 29

Azure AI Fundamentals (AI-900) Study Guide_ In-Depth Exam -- Tom Taulli -- 1, 2025 -- O’Reilly
$ 4.5
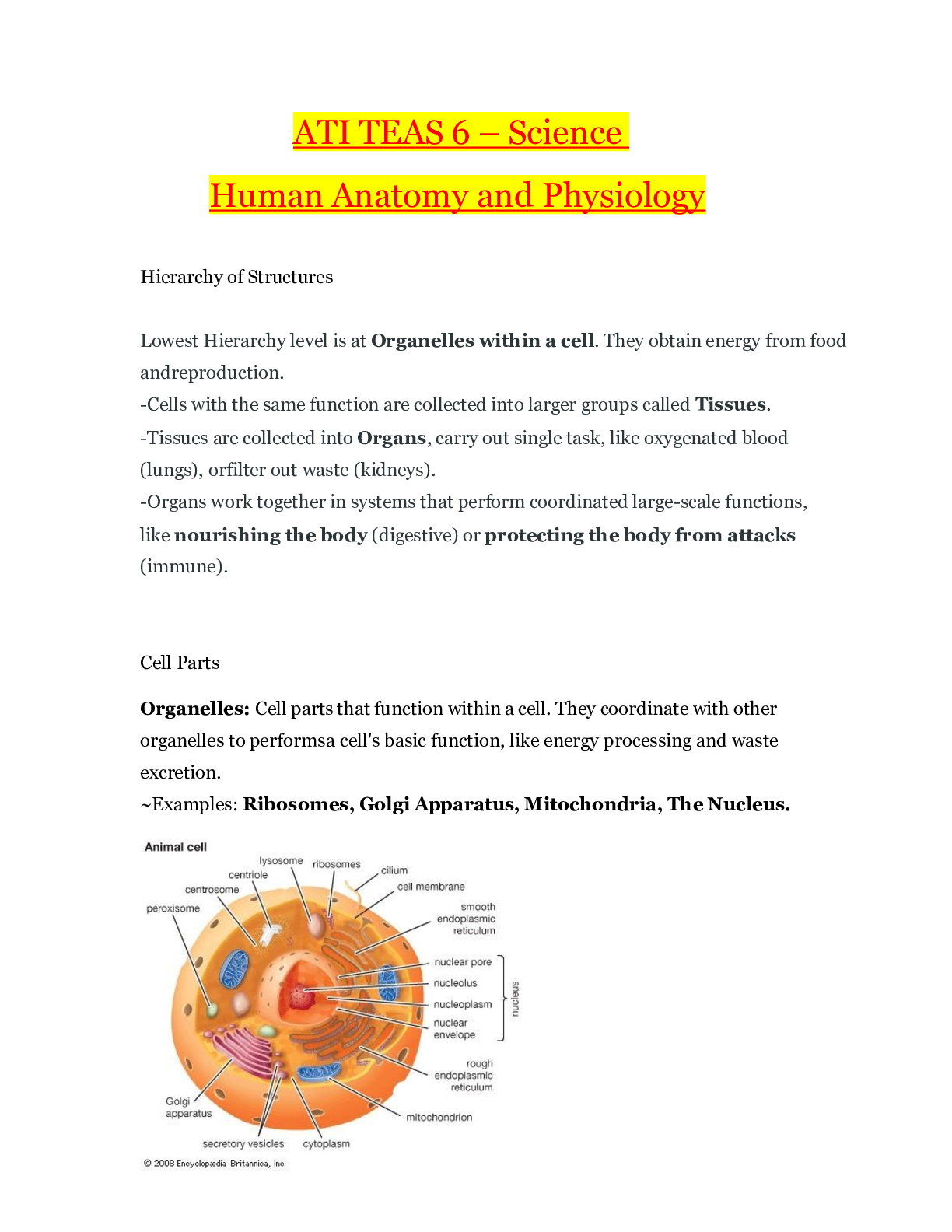
ATI TEAS 6 – Science Human Anatomy and Physiology-revised to ace your study
$ 13

Case study
$ 50

ITT Tech Pittsburgh - IS 4560IS4650 Project
$ 7

CSIS 330 Quiz 1 Liberty University answers complete solutions;Latest 2019/20.
$ 5

AC 221 TAXATION II REVIEW EXAM Q & A 2024
$ 15

PSYC F21 Final TESTBANK
$ 18

PHIL 347 Week 1 - Discussion, Wisdom vs Knowledge
$ 5

Instructor Manual for Automotive Engines Diagnosis, Repair, and Rebuilding 9th Edition By Tim Gilles, Tim LeVan (All Chapters, 100% Original Verified, A+ Grade)
$ 13

Comprehensive i-Human Virtual Patient Case (2026): Evaluation and Evidence-Comprehensive i-Human Virtual Patient Case (2026): Evaluation and Evidence Based Management of a NewOnset Rash, Integrating History, Physical Examination, Differential Diagnosis, T
$ 19

ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM
$ 20

SU_NSG6430_Holloway_Freeman_O._week_7.pptx.pdf
$ 15

AQA 2022. A-level PSYCHOLOGY Paper 3 Issues and options in psychology
$ 8

ATI Content Mastery Series Assessments- RN Pharmacology Practice Assessment A




























