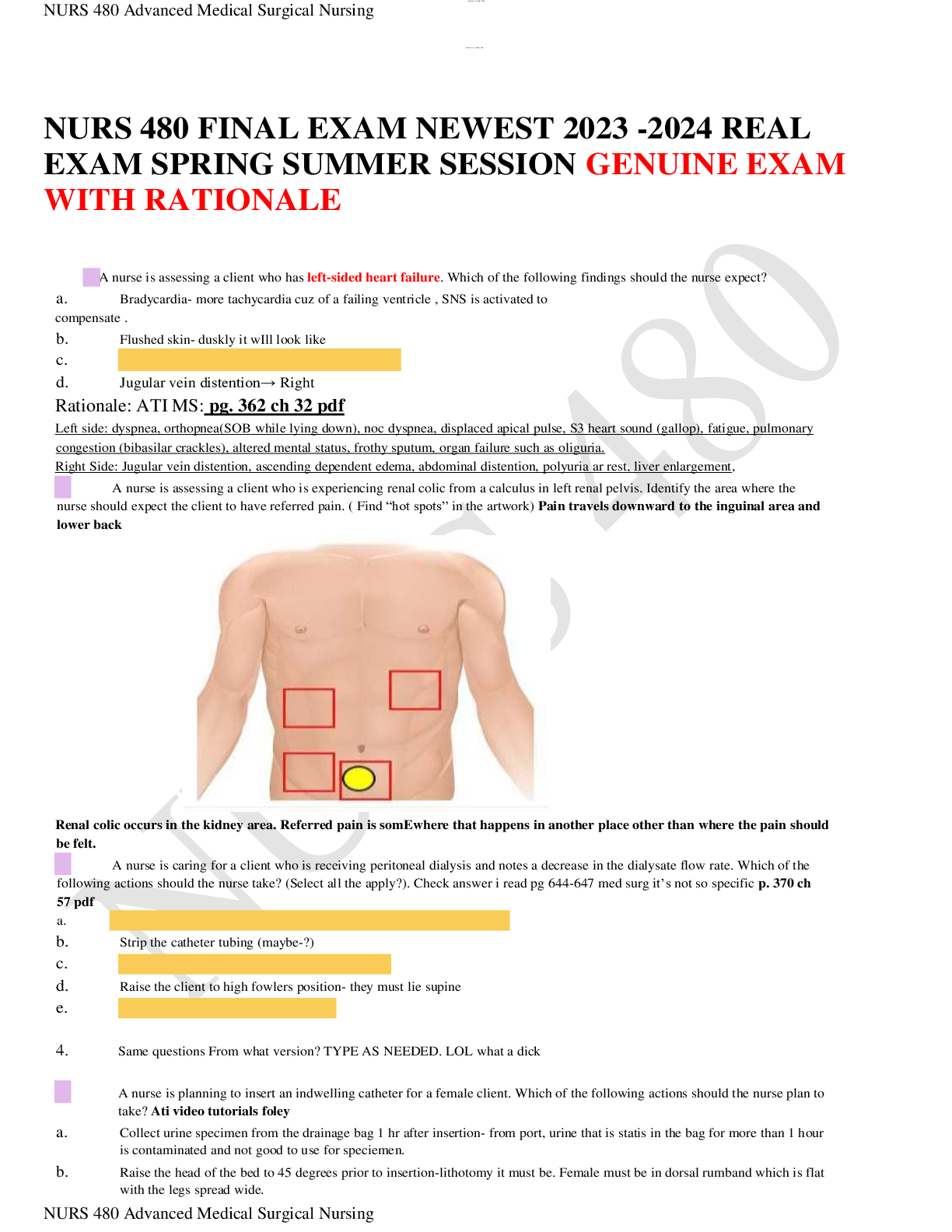
Mark Klimek Audio Notes: Acid Base ABG’s
As pH goes, so does my Pt! Except for K
pH and HCO3 in same direction Metabolic
pH and HCO3 in different direction: Respiratory
pH ↓ Pt goes ↓ (HR, RR, all vitals) K goes ↑ hy
...
Mark Klimek Audio Notes: Acid Base ABG’s
As pH goes, so does my Pt! Except for K
pH and HCO3 in same direction Metabolic
pH and HCO3 in different direction: Respiratory
pH ↓ Pt goes ↓ (HR, RR, all vitals) K goes ↑ hypoexcitable
pH ↑ Pt goes ↑ K goes ↓ hyperexcitable
Except for K – it does the opposite
pH ↑ : Alkalosis
Seizures, hyperactivity, borborgygmi (↑BS)
Kausmal breathing = MacKausamal (Metabolic Acidosis breathing)
Causes of imbalance:
1. Is lung affected?
a. Yes-Respiratory
2. Is pt overventilating or underventilating?
a. Over-alkalosis
b. Under-acidosis
3. Not the lung?
a. Then it is Metabolic
4. If pt has prolonged vomiting or suctioning
a. Alkalosis
5. If you don’t know: it’s probably metabolic acidosis (It’s super common)
Alcoholism
Psychological
#1 problem psychologically in alcoholism and all other abusers is denial
Denial-refusal to accept the reality of a problem
o Treat denial by confronting
o Differentiate what they say versus what they do
DO NOT confuse confrontation with aggression (attacks the person)
Questions about staff problem interactions: Never choose YOU, choose I
Denial is okay in loss/grief
o Treat this denial with support-Do NOT confrontMark Klimek Audio Notes 2
Denial Anger Bargaining Depression Acceptance
#2 problem dependency/codependency
o Dependency-abuser gets significant other to do things for them
o Codependency-positive self esteem significant other receives from doing things for the
abuser
o Treat by setting limits and enforce them, say no
Manipulation-abuser gets significant other for to do things them that is not in the best interest of the
SO
o Interest and harmful
o If what being asked to do is neutral-dependency
o If what being asked is harmful or not in best interest-manipulation
o Treat manipulation by setting limits and enforce, say no
Wernicke’s and Korsakoff
o Wernickes’-encephalopathy induced by vit B1/ thiamine deficiency
o Korsakoff-psychosis induced by vit B1/ thiamine deficiency
Primary symptom- amnesia with confabulation
Redirect pt to other things
Preventable-take vitamin B1/thiamine
Arrestable-take vitamin B1/thiamine
Irreversible
Antabuse (disulfiram) and Revia (naltrexone)
o Aversion therapy
o Onset: 2 weeks, Duration 2 weeks
o Pt teaching
avoid all forms of alcohol-mouthwash, aftershave, perfumes/colognes/ insect
repellants, OTC ending with elixir, alcohol based hand sanitizer, uncooked icing
DO NOT pick red wine vinaigrette
Overdose and Withdrawal
o Every abused drug is either upper or downer
o 1. Is drug upper or downer?
Upper: caffeine, cocaine, pcp/lsd, methamphetamines, Adderall (amphetamine)
Things go up: euphoria, tachycardia, restlessness, irritability, borborygmic,
diarrhea, hypereflexia 3+ or 4+, seizures (have suction at bedside)
Downer: If not upper, it is a downer
Things go down: lethargic, bradycardia, respiratory arrest (have ambu-bag
at bedside)
o 2. Overdose or withdrawal?
Overdose/intoxication-Overdose on an upper- everything goes up
Overdose downer- everything goes down
Withdrawal downer-everything go up
Wthdrawal upper-everything go down
Drug Addiction in Newborns
o Always assume intoxication not withdrawal at birth (before 24 hours)
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome vs delirium tremens (DT)Mark Klimek Audio Notes 3
o Every alcoholic goes through alcohol withdrawal after 24 hr of not drinking, only minority go
through DT (72 hrs)
o Alcohol withdrawal-not life-threatening, not a danger to self or others
o DT-life-threatening, danger to self and others
AWS DT
Regular diet NPO; clear liquids
Semi-private anywhere Private, near nurse’s station
No restraints Restricted bedrest (bedpans, urinals)
Must be restrained (vest or 2 point lock
leather)
Antihypertensive/tranquilizer/Vitamin B1 Antihypertensive/tranquilizer/Vitamin B1
Ventilators
High Pressure Alarm
Obstruction-Increased resistance to airflow
o Kinks (unkink)
o Water condensation (open system and drain tubing)
o Mucous secretions in airway (TCDB, suction)
Low Pressure Alarm-↓ Resistance – machine finding job too easy
Disconnected
o Main tubing (reconnect)
o Oxygen sensor (reconnect)
If tube goes lower than pt level – contaminated
Ventilator overventilating pt can result in resp. alkalosis
Ventilator underventilating pt can result in resp. acidosis
Amino Glycosides
A Mean Old Mycin
Amino Glycosides only treat Mean old Infections!
Serious, resistant, gram-negative, life-threatening
True mean old Mycins don’t have “Thro”
If it has “Thro” – Thro it away!
Ex: Zithromycin , erythromycin, clarithromycin
Mean Old Mycins (mice) destroy ears (ototoxicity) and kidneys (nephrotoxicity)
Must check Creatinine (0.6 -1.3) for Nephrotoxicity – NOT urine output
Check hearing, tinnitus, vertigo, dizzinessMark Klimek Audio Notes 4
8 Toxic to Cranial nerve 8 (vestibulocochlear) give q8h, IM/IV
Mean Old Mycins do NOT get absorbed – they go in and out and sterilize/clean
Hepatic (encephalopathy)coma-reduce ammonia levels. Oral mycins redcues ammonia
PO Mean Old Mycins are for bowel sterilizing
NeoMYCIN
KanoMYCIN
Who can sterilize my bowel?? NEO KAN!
Drawing TAP Levels (Peak and Trough)
For drugs that have a narrow therapeutic window/level and are toxic
Digitalis
Route determines TAP – Not the drug
TROUGH PEAK
IV 30 MIN BEFORE NEXT DOSE IV 15-30 min after its done
IM 30 MIN BEFORE NEXT DOSE IM 30-60 min after its given
SubQ-See
SUB Q 30 MIN BEFORE NEXT DOSE Subling 5-10 min after its in the system
PO 30 MIN BEFORE NEXT DOSE No PO peak
Heart Rhythms
Calcium channel blockers are like valium for the heart
Ca Channel Blockers are chill pills for the heart
They end in -DEPINE or ZEM
Verapamil, Cardizem (Cardizem can be continuous IV drip)
Calcium channel blockers are negative inotropic, negative chronotropes, negative dromotropes- fancy way of
saying valium for the heart
Positive inotropes- are cardiac stimulant
Negative- cardiac depressantsMark Klimek Audio Notes 5
Calcium Channel Blockers Treats:
Antihypertensive
Antianginals
Antiatrial Arrythmia
Side Effects: Headache, Hypotension
Measure BP: Hold if systolic <100
Rhythms
Normal sinus rhythm
Ventricular fibrillation
Vfib: Chaotic without QRS pattern – Lethal (No cardiac output)
Ventricular tachycardia
Vent tachy: Wide bizarre QRS -Potentially lethal (Has cardiac output)
Bizarre-tachycardia
Asystole
Asystole: No QRS – Lethal (No cardiac output)
QRS depolarization-Ventricular
P wave-atrial related
Flutter: SawtoothMark Klimek Audio Notes 6
Afib: Chaotic with QRS pattern
SVT: Narrow QRS
PVC: random rhythm change – Periodic wide and bizarre QRS-PVC.
Only concerned if1:
More than 6,
6 in a row,
PVC falls on t wave on the previous beat
Change in rhythm: check pulse or BP for cardiac output
Treat ventriculars (PVC, Vtach) with lidocaine/amiodarone
V → L
Treat SVT (it’s actually an atrial)
A denosine –PUSH it fast; puts you in asystole for 20-30 seconds
B eta blockers – all end it “lol”. Side effect: headache, hypotension
C a channel blockers
D igitalis (lanoxin)-
VFib: you DFib
Asystole: epinephrine then atropine
Chest Tubes
Re-establish negative pressure in the pleural space
The only chest surgery that doesn’t require a chest tube is a pneumonectomy – because you remove the
entire lung
A. Pneumothorax- apical air; Needs to bubble
B. Hemothorax- basilar blood; Report no drainage from chest tube, no bubbles
C. Pneumohemothorax-Blood and air
Knock System Down
1. Pick system back up
2. Have pt take a few deep breaths
Water seal breaks
1. Clamp
2. CutMark Klimek Audio Notes 7
3. Put in sterile water
4. Unclamp
Chest tube comes out
1. Cover with gloved hand
2. Vaseline gauze
3. Sterile dressing taped on 3 sides
Bubbling: Where? When?
Water Seal
Intermittent: good; document
Continuous: bad (air leak)
Suction Control
Intermittent: bad (dial up suction)
[Show More]