WGU C175 Data Management – Terms,
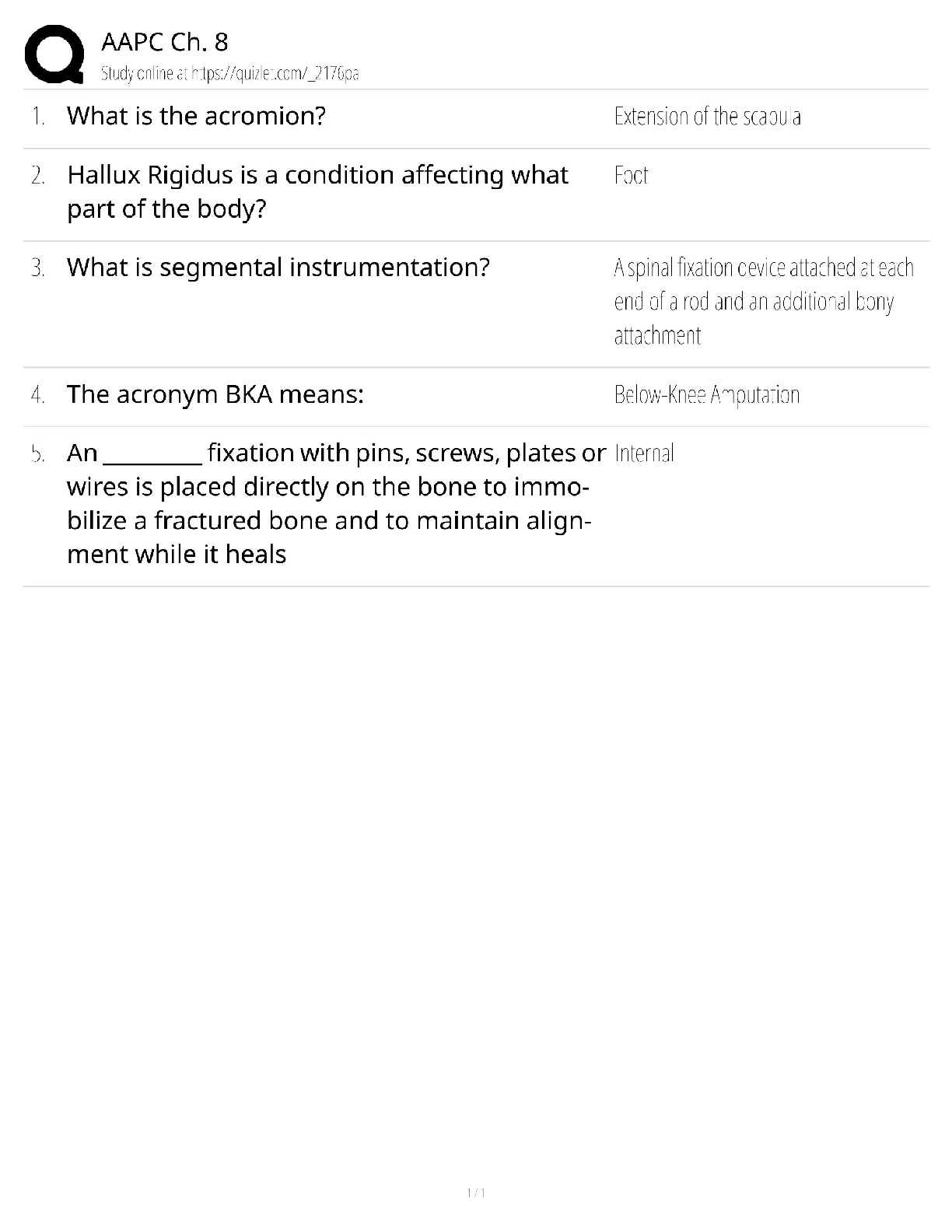
100% Accurate, graded A+
Big Data - ✔✔-Refers to data sets whose sizes are beyond the capability of commonly used software
tools to capture, store, manage and process within acceptab
...
WGU C175 Data Management – Terms,
100% Accurate, graded A+
Big Data - ✔✔-Refers to data sets whose sizes are beyond the capability of commonly used software
tools to capture, store, manage and process within acceptable time limits.
Data - ✔✔-Facts gathered together for analysis - Collection of raw facts from which conclusions might
be drawn.
Data Center - ✔✔-A facility that contains information storage and other physical information technology
(IT) resources for computing, networking, and storing information.
Data Explosion - ✔✔-Inexpensive and easier ways to create, collect, and store all types of data, coupled
with increasing individual and business needs, have led to accelerated growth.
Data Science - ✔✔-Enables organizations to derive business value from Big Data.
Data Storage - ✔✔-Devices designed for storing data
Digital Data - ✔✔-Stored as things of binary numbers (0s and 1s)
Flat Files - ✔✔-A file having no internal hierarchy
Hashed Files - ✔✔-A file that has been encrypted for security purposes.
Heap Files - ✔✔-An unsorted set of records
Information - ✔✔-The transformation of raw data into useful facts.
Punch card - ✔✔-A card that is perforated and can hold commands or data.
Structured Data - ✔✔-Information with a high degree of organization. Organized in rows and columns in
a rigidly defined format. Typically stored using a database management system (DBMS).
Unstructured Data - ✔✔-Information that does not have structure (such as text).
Attribute - ✔✔-A property or characteristic of an entity. Employee number, weight of an automobile,
company's address, or date of sales meeting.
Binary Relationship - ✔✔-It is a relationship between two entity types.
Cardinality - ✔✔-It is the maximum number of entities that can be involved in a particular relationship.
E-R Model - ✔✔-It is well named, as it diagram entities (together with their attributes) and the
relationships among them.
Entity - ✔✔-Object or event in our environment that we want to keep track of. Person, building, piece of
inventory on a shelf, finished product ready for sale, sales meeting or an event.
Intersection data - ✔✔-The combination of or the association between a particular entity and another.
Modality - ✔✔-It is a minimum number of entity occurrences that can be involved in a relationship.
One-to-One Binary Relationship - ✔✔-It means that a single occurrence of one entity type can be
associated with a single occurrence of the other entity type and vice versa.
Ternary Relationship - ✔✔-A ternary relationship involves three different entity types.
Unary Relationship - ✔✔-It is an associate occurrence of an entity type with other occurrences of the
same entity type.
Unique Identifier - ✔✔-It is used to uniquely identify each record in a database table.
Candidate Key - ✔✔-If a relation has more than one attribute or minimum group of attributes that
represents a way of uniquely identifying the entities, then they are each called a candidate key.
Computer Security - ✔✔-It includes protecting the physical hardware environment, defending against
hacker attacks, encrypting data transmitted over networks, educating employees on the important of
protecting the company's data, and many more.
Concurrency Problem - ✔✔-If two or more users are trying to update a particular record simultaneously,
they run the risk of generating what is known as a "concurrency problem."
Data Integration - ✔✔-It refers to the ability to tie together pieces of related data within an information
system.
Data Redundancy - ✔✔-It refers to the same fact about the business environment being stored more
than once within an information system.
Data Retrieval - ✔✔-It involves the fetching of desired data from a database.
Direct Access - ✔✔-It is a retrieval of a single record of a file or subset of the records of a file based on
one or more values of a field or a combination of fields in the file.
Entity Set - ✔✔-A collection of entities of the same time (e.g., all the company's employees).
Equijoin - ✔✔-Combines two or more tables based on a column that is common to the tables.
Fields - ✔✔-Columns representing the facts.
File - ✔✔-The entire structure.
Foreign Key - ✔✔-If, in a collection of relations that make up a relational database, an attribute or group
of attributes serves as the primary key of one relation and also appears in another relation, then it is
called a foreign key in that other relation.
JOIN operator - ✔✔-It specifies how to relate tables in the query.
Logical Sequential Access - ✔✔-Records are retrieved in order based on the values of one or a
combination of the fields.
Natural Join - ✔✔-Matches each row in a table against each row in another tabled based on common
values found in columns sharing a common name and data type.
Physical Sequential Access - ✔✔-Records are retrieved one after the other, just as they are stored on the
disk device.
Primary Key - ✔✔-It is an attribute or group of attributes whose values are unique throughout all rows
of the relation.
Record - ✔✔-A collection of related data items.
Reengineering - ✔✔-Data and information systems are aggressively used to redesign business processes
for maximum efficiency.
Relational Algebra - ✔✔-It is a formal system for manipulating relations.
Retrieve or Read - ✔✔-It refers to the data without changing
[Show More]