Est ISYE 6501 Lecture Transcripts
About This Document
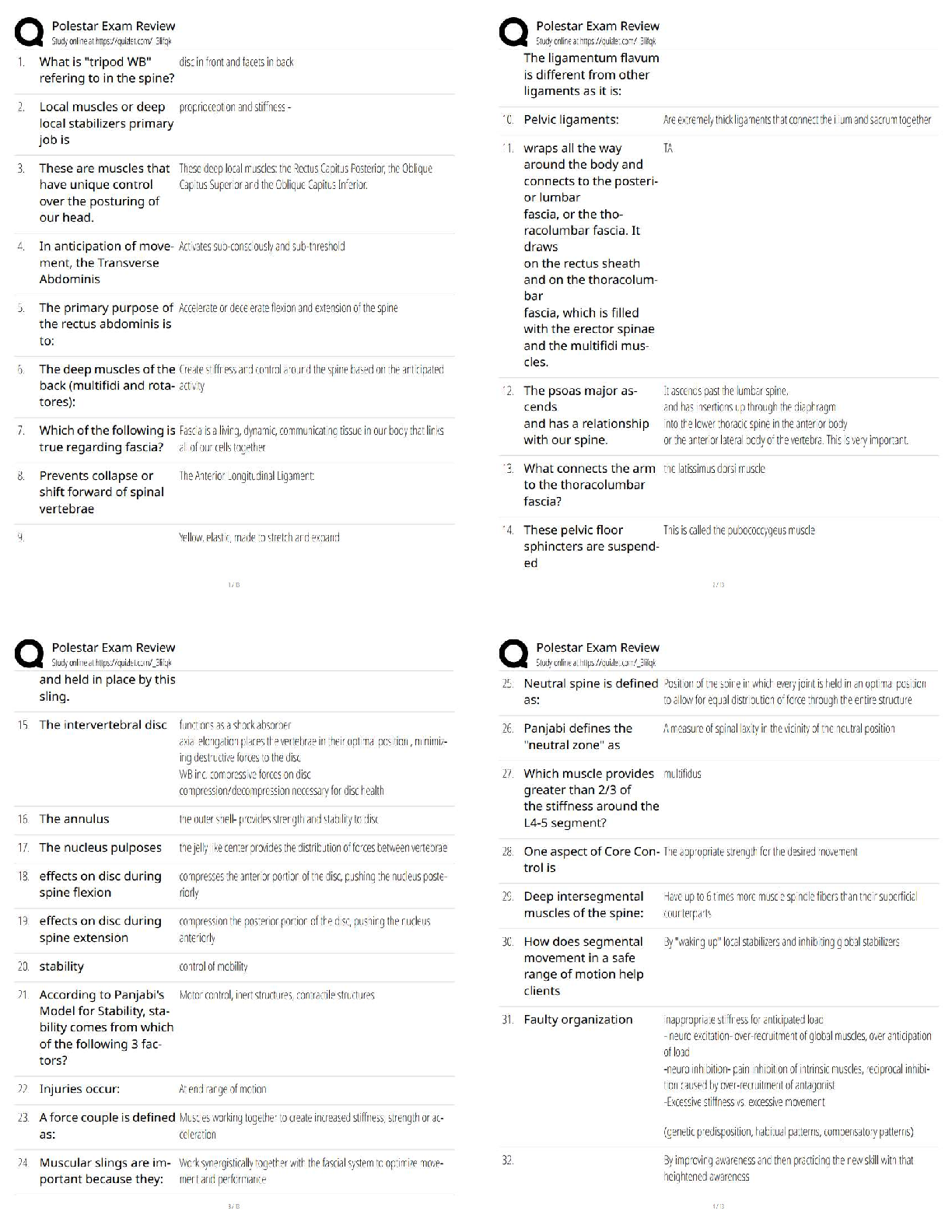
This document was originally created in the summer of 2017 and is maintained
collaboratively through the efforts of the students of edX GTx ISYE 6501 using
transc
...
Est ISYE 6501 Lecture Transcripts
About This Document
This document was originally created in the summer of 2017 and is maintained
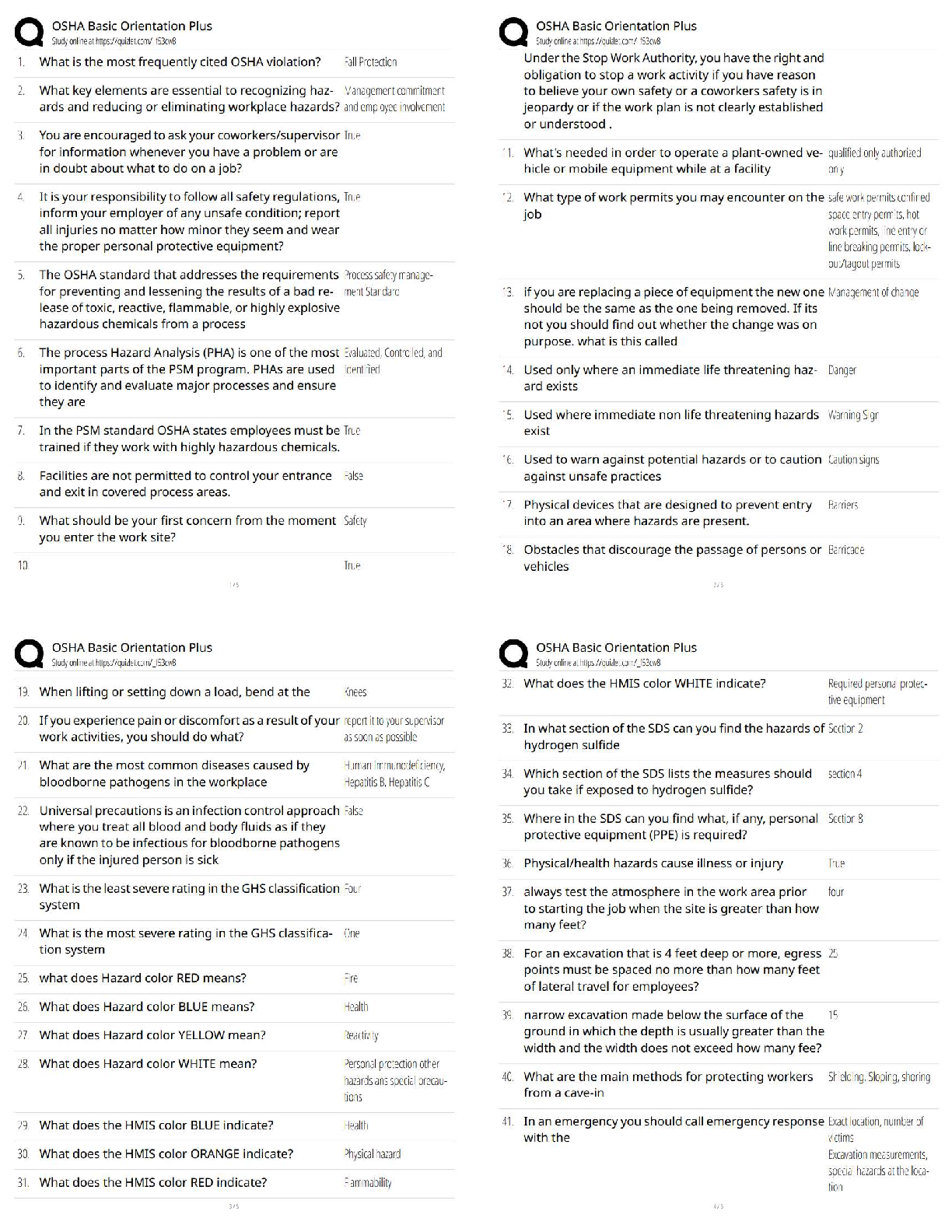
collaboratively through the efforts of the students of edX GTx ISYE 6501 using
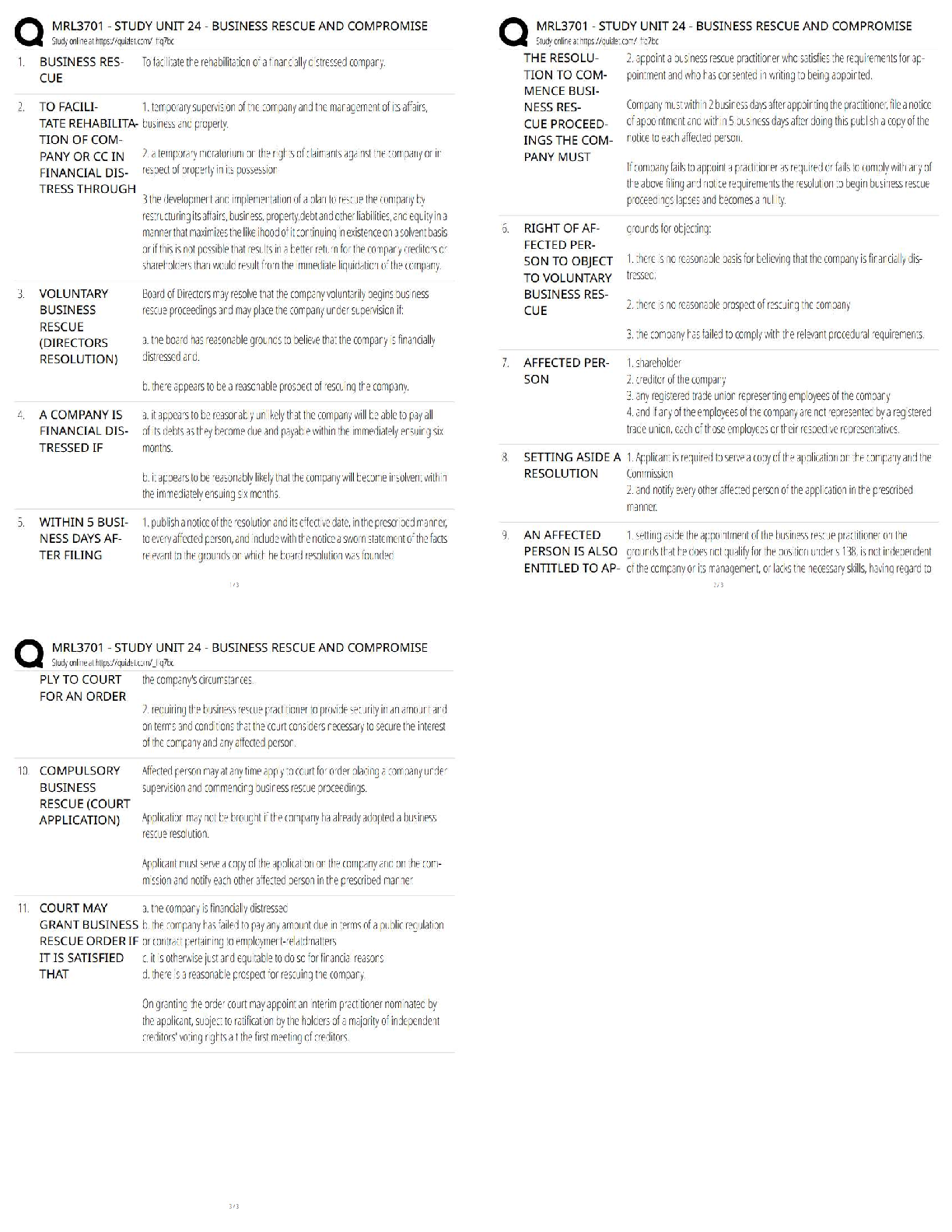
transcripts and screenshots from the video lectures. You are strongly encouraged to
improve the formatting, layout, add or adjust images, bold key words, and even
condense copy and remove personal asides (sorry, Professor Sokol).
It is expected that sections may be added, removed, or modified -- in which case,
again, you should please take the liberty of adjusting this document to match.
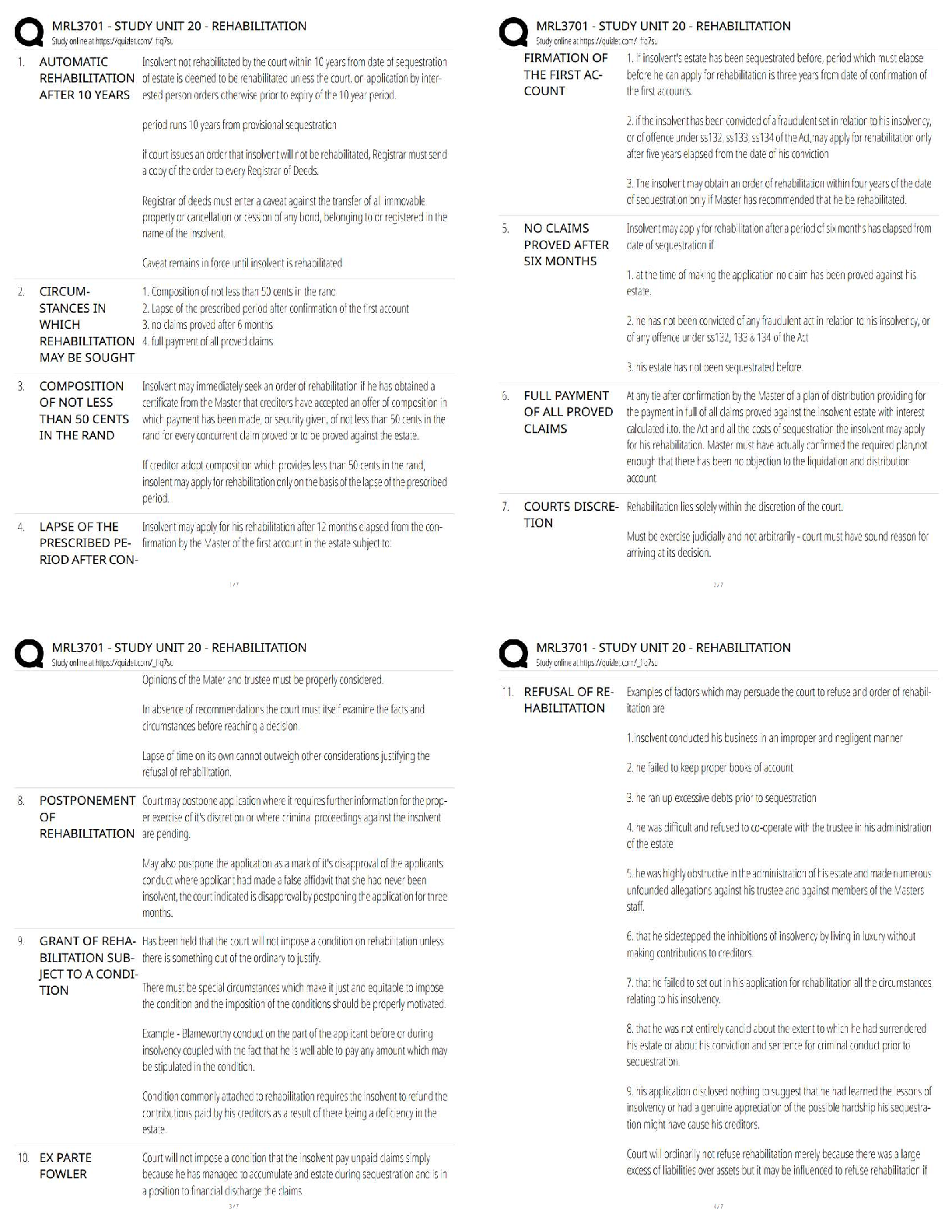
Some tips on formatting: the Weeks (e.g., Week 1), Modules (e.g., 1. Introduction),
and Sub-Modules (e.g., 1.3 (C): What is Modeling?) are formatted respectively as
Heading 1, Heading 2, and Heading 3. These can be adjusted in the format menu, or
by pressing Ctrl + 1, Ctrl + 2, and Ctrl + 3, respectively, while the cursor is on the
line you wish to change.
Pressing Ctrl + , will toggle subscript text on and off.
For use as study material for GTx 6501x. Text and images copied directly from the course videos, with light
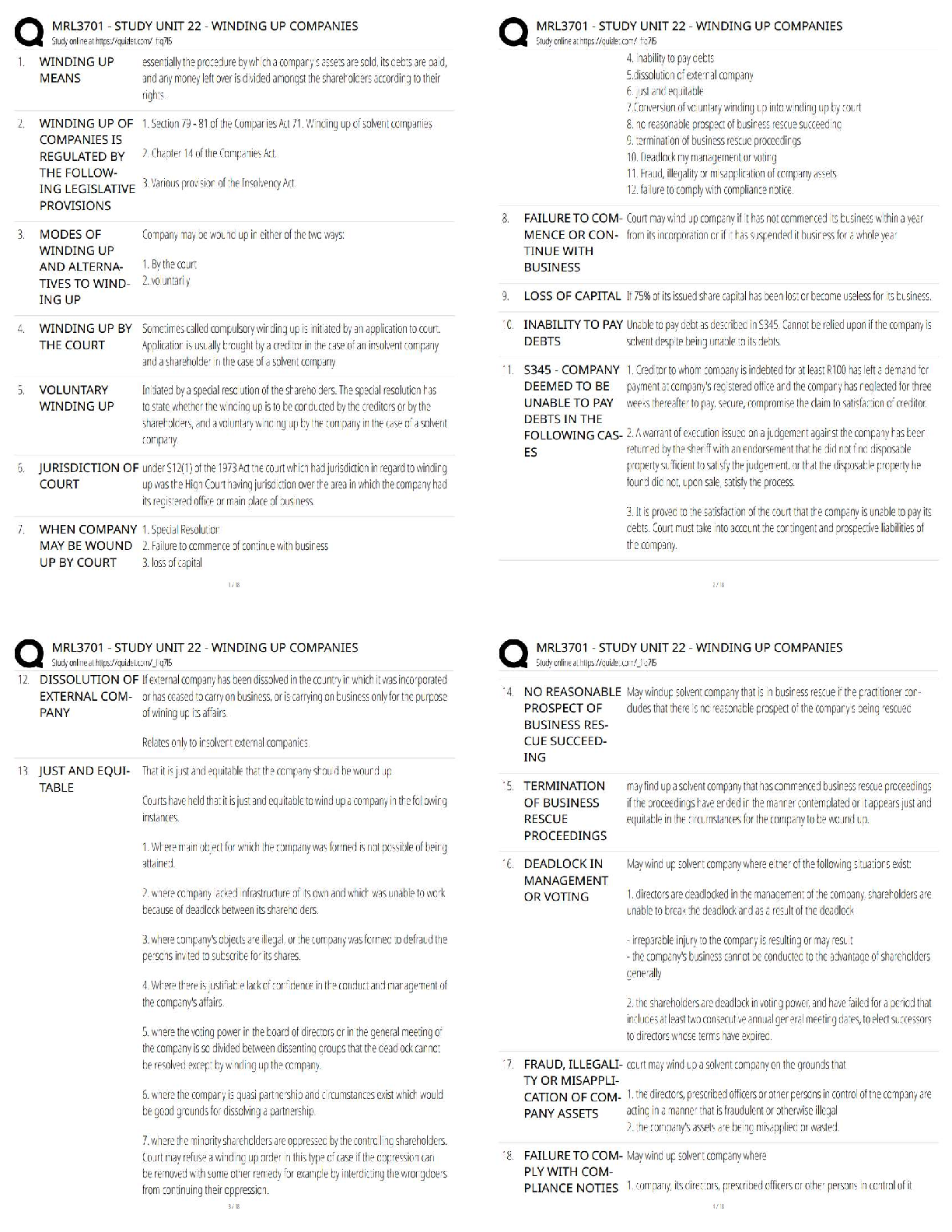
editing for readability. Not intended for broad distribution or general use.
Content is the intellectual property of Joel Sokol and Georgia Tech.
1ISYE 6501 Lecture Transcripts 0
About This Document 0
Week 1 6
1. Introduction 6
1.1 (C): Introduction to Analytics Modeling 6
1.2 (C): Introduction to the Course 9
1.3 (C): What is Modeling? 11
2. Classification 12
2.1 (M): Introduction to Classification 12
2.2 (M): Choosing a Classifier 14
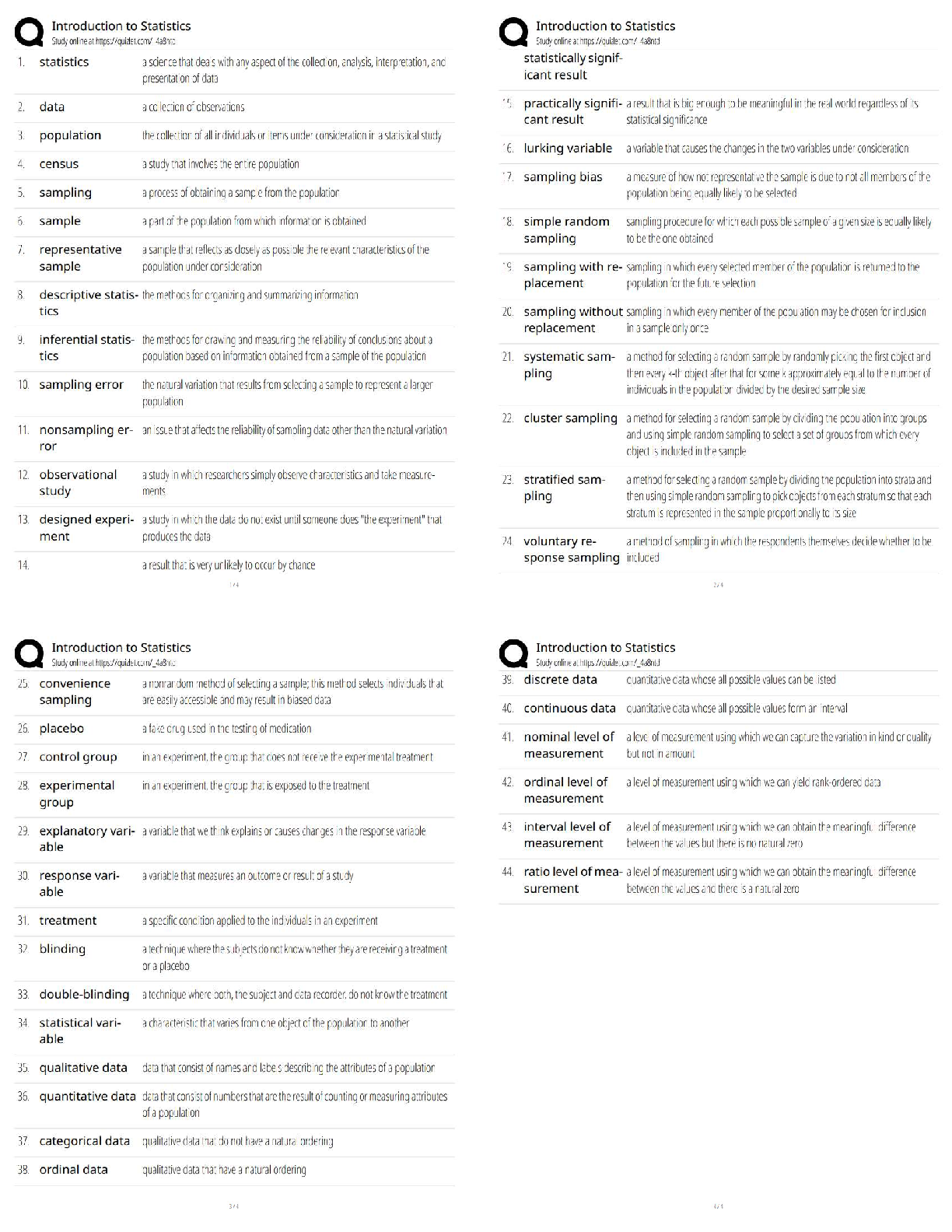
2.3 (C): Data Definitions 19
2.4 (M): Support Vector Machines (SVM) 21
2.5 (M): SVM: What the Name Means 25
2.6 (M): Advanced SVM 27
2.7 (C): Scaling and Standardization 30
2.8 (M): K-Nearest Neighbor Classification 33
Week 2 35
3. Validation 35
3.1 (C): Introduction to Validation 35
3.2 (C): Validation and Test Data Sets 37
3.3 (C): Splitting Data 39
3.4 (C): Cross-Validation 41
4. Clustering 43
4.1 (M): Introduction to Clustering 43
Examples of Clustering 43
[IMAGE] 44
[IMAGE] 44
4.2 (C): Distance Norms 45
4.3 (M): K-means Clustering 48
4.4 (M): Practical Details for K-Means 50
4.5 (M): Clustering for Prediction 52
4.6 (M): Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning 54
2Week 3 55
5. Basic Data Preparation 55
5.1 (C): Introduction to Data Preparation 55
5.2 (C): Outlier Detection 56
[IMAGE] 56
[IMAGE] 56
[IMAGE] 57
[IMAGE] 57
[IMAGE] 57
5.3 (C): Dealing with Outliers 58
6. Change Detection 60
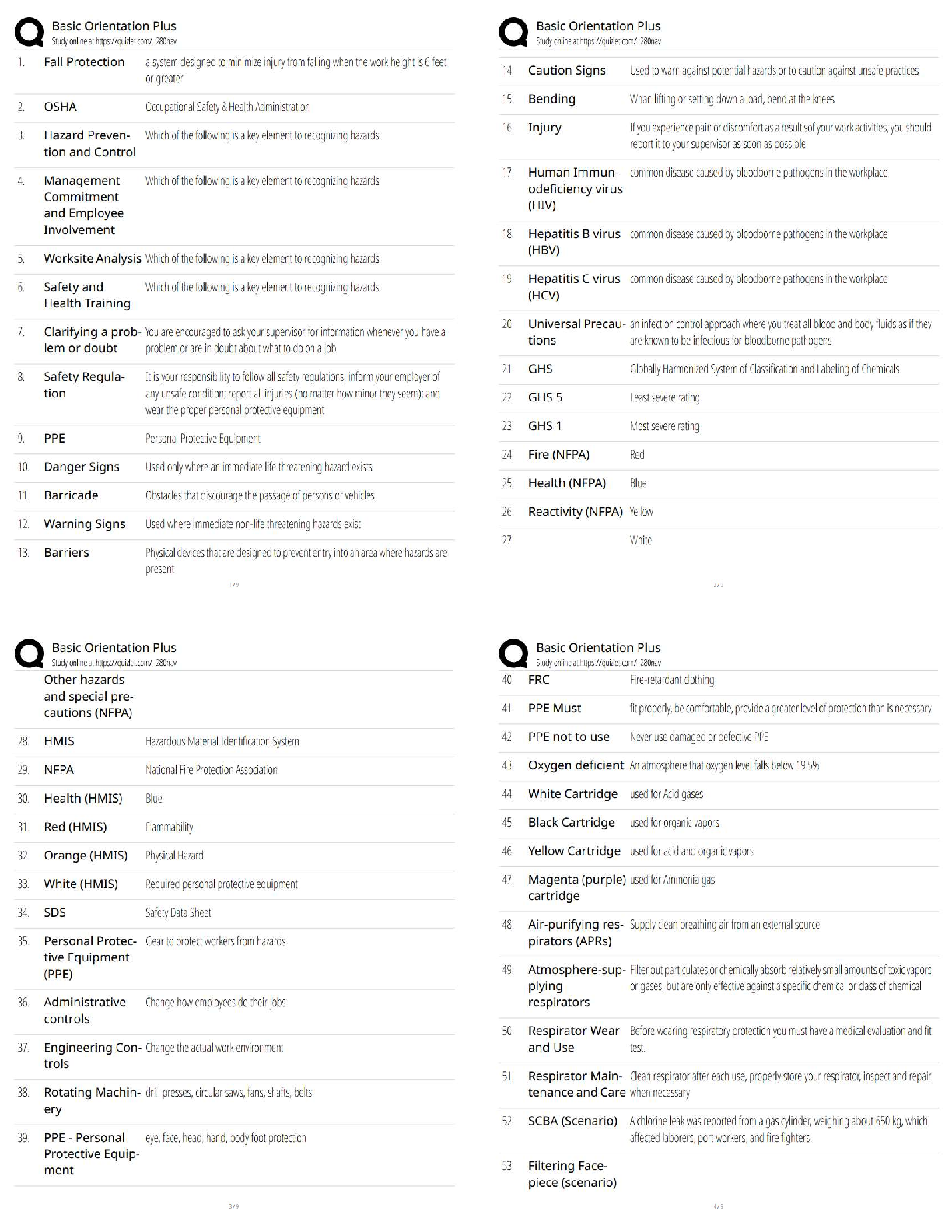
6.1 (M): Introduction to Change Detection 60
Case Study: Semiconductor Manufacturing Traffic 60
Case Study: Railroad Safety 61
[IMAGE] 61
[IMAGE] 61
6.2 (M): CUSUM for Change Detection 62
[IMAGE] 63
[IMAGE] 63
[IMAGE] 63
[IMAGE] 64
6.3 (M): Change-Detection Homework Follow-up 65
Week 4 67
7. Time Series Models 67
7.1 (M): Introduction to Exponential Smoothing 67
7.2 (M): Trends and Cyclic Effects 71
[FORMULA SCREENCAP] 71
7.3 (M): Exponential Smoothing: What The Name Means 76
[IMAGE] 76
7.4 (M): Forecasting 78
7.5 (M): ARIMA 80
7.6 (M): GARCH 85
[IMAGE] 85
3Week 5 87
8. Basic Regression 87
8.1 (M): Introduction to Regression 87
[IMAGE] 87
[IMAGE] 88
8.2 (C): Maximum Likelihood and Information Criteria 90
8.3 (M): Using Regression 93
8.4 (C): Causation vs Correlation 95
8.5 (M): Transformation and Interactions 98
8.6 (M): Regression Output 99
Week 6 101
9. Advanced Data Preparation 101
9.1 (C): Box-Cox Transformation 101
9.2 (C): De-Trending 103
9.3 (C): Introduction to Principal Component Analysis 105
9.4 (C): Using Principal Component Analysis 107
9.5 (C): Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 109
Week 7 109
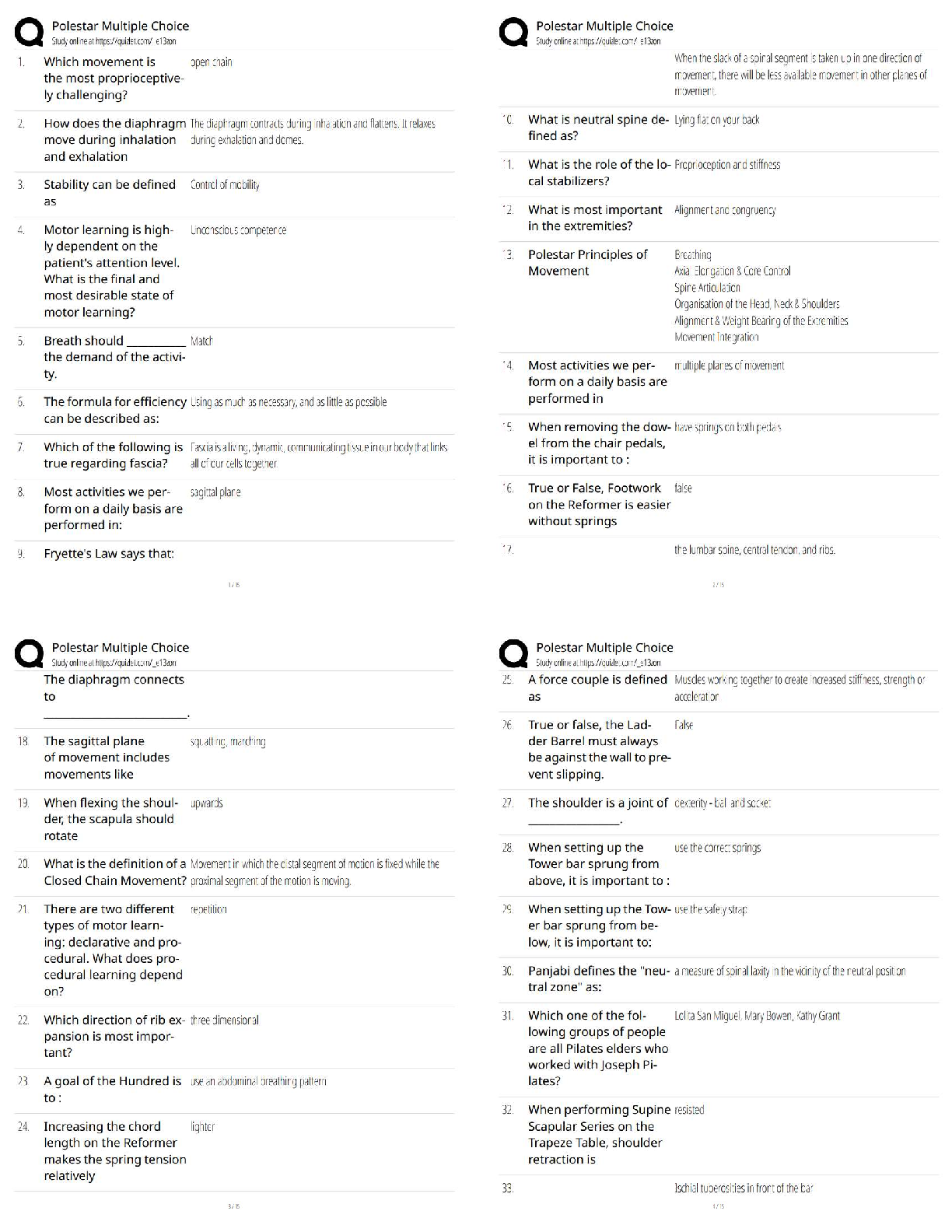
10. Advanced Regression 110
10.1 (M): Introduction to CART 110
10.2: (M): Branching 112
10.3: (M): Random Forests 114
10.4: (M): Logistic Regression 116
10.5: (C): Confusion Matrices 119
10.6: (C): Situationally-Driven Comparison 122
10.7: (M): Advanced Topics in Regression 124
Week 8 126
11. Variable Selection 126
11.1: (C): Introduction to Variable Selection 126
11.2: (C): Models for Variable Selection 129
11.3: (C): Choosing a Variable Selection Model 133
12. Design of Experiments 136
12.1 (M): Introduction to Design of Experiments 136
412.2 (M): A/B Testing 138
Case Study: Banner Ad Test 138
12.3 (M): Factorial Designs 140
12.4 (M): Multi-Armed Bandits 143
13. Probability-Based Models 145
13.1 (M): Introduction to Advanced Probability Distributions 145
Case Study: Baseball Ticket Upgrades 145
13.2 (M): Bernoulli, Binomial and Geometric Distributions 147
13.3 (M): Poisson, Exponential and Weibull Distributions 151
Case Study: Atlanta Airport Arrivals 152
13.4 (C): Q-Q Plots 155
13. Probability-Based Models, Continued 158
13.5 (M): Queuing 158
13.6 (M): Simulation Basics 161
13.7 (M): Prescriptive Simulation 164
13.8 (M): Markov Chains 166
14. Missing Data 168
14.1 (C): Introduction to Missing Data 168
14.2 (C): Methods That Do Not Require Imputation 171
Method 1. Throw Away Data 171
Method 2. Use Categorical Variables 171
14.3 (C): Imputation Methods 173
Imputation Method: Use An Average 173
Imputation Method: Use A Predictive Model 173
Imputation Method: Perturbation 174
15. Optimization 176
15.1 (M): Introduction to Optimization 176
15.2 (M): Elements of Optimization Models 178
15.3 (M): Modeling is an Art: Two Examples 180
Case Study: The Army Diet Problem 180
15.4 (M): Modeling With Binary Variables 183
Week 9 184
15.5 (M): Optimization for Statistical Models 186
15.6 (M): Classification of Optimization Models 189
515.7 (M): Stochastic Optimization 192
15.8 (M): Basic Optimization Algorithms 195
16.1 (M): Non-Parametric Methods 197
16.2 (M): Bayesian Modeling 200
16.3 (M): Communities in Graphs 204
16.4 (M): Neural Networks and Deep Learning 207
16.5 (M): Competitive Models 209
16.5a (M): Competitive Models Demo 212
Week 10 215
17.1 A Format For Discussion 216
18.1 Introduction to Power Company Case 217
18.2 Models for Customer Identification 218
18.3 (X): Models for Cost Estimation 220
18.4 (X): Models for Shutoff Selection 222
Week 11 222
19.1 (X): Introduction to Retailer Case 22
[Show More]