C785 Biochem Study Guide-comprehensive-2022
Amino Acids, Peptide Bonds & Protein Structure
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules:
Most important large molecules found in living things – ca
...
C785 Biochem Study Guide-comprehensive-2022
Amino Acids, Peptide Bonds & Protein Structure
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules:
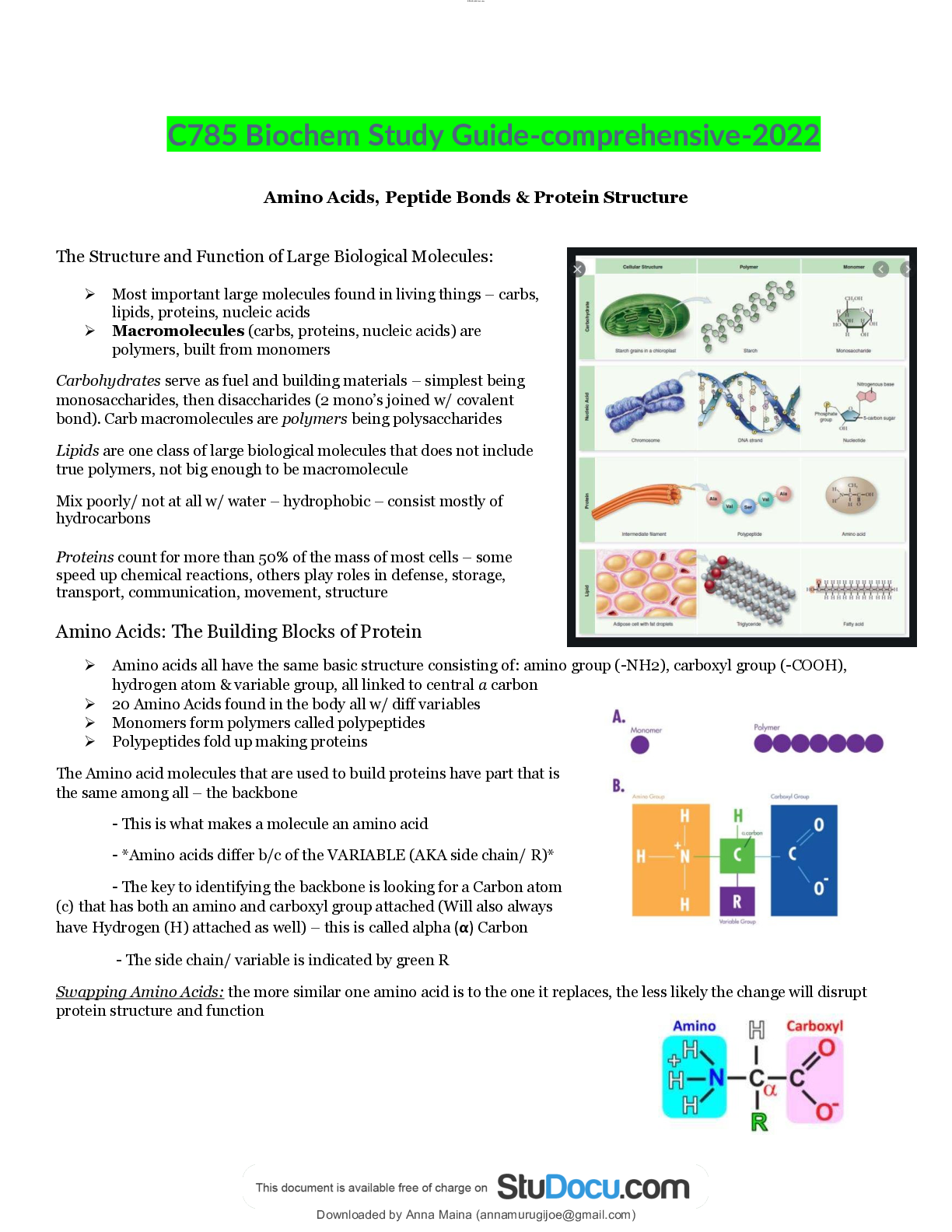
Most important large molecules found in living things – carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Macromolecules (carbs, proteins, nucleic acids) are polymers, built from monomers
Carbohydrates serve as fuel and building materials – simplest being monosaccharides, then disaccharides (2 mono’s joined w/ covalent bond). Carb macromolecules are polymers being polysaccharides
Lipids are one class of large biological molecules that does not include true polymers, not big enough to be macromolecule
Mix poorly/ not at all w/ water – hydrophobic – consist mostly of hydrocarbons
Proteins count for more than 50% of the mass of most cells – some speed up chemical reactions, others play roles in defense, storage, transport, communication, movement, structure
Amino Acids: The Building Blocks of Protein
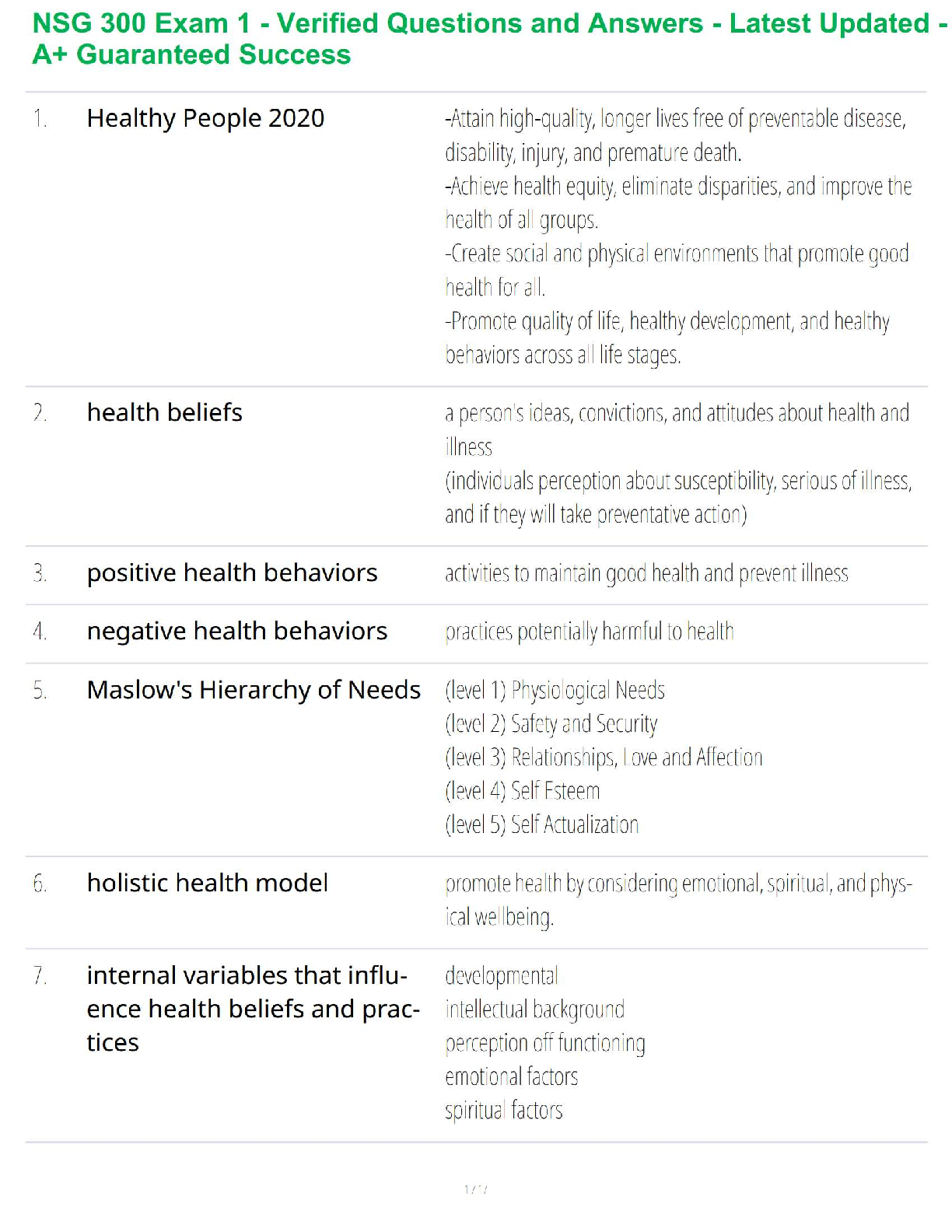
Amino acids all have the same basic structure consisting of: amino group (-NH2), carboxyl group (-COOH), hydrogen atom & variable group, all linked to central ? carbon
20 Amino Acids found in the body all w/ diff variables
Monomers form polymers called polypeptides
Polypeptides fold up making proteins
The Amino acid molecules that are used to build proteins have part that is the same among all – the backbone
- This is what makes a molecule an amino acid
- *Amino acids differ b/c of the VARIABLE (AKA side chain/ R)*
- The key to identifying the backbone is looking for a Carbon atom
(c) that has both an amino and carboxyl group attached (Will also always have Hydrogen (H) attached as well) – this is called alpha (?) Carbon
- The side chain/ variable is indicated by green R
Swapping Amino Acids: the more similar one amino acid is to the one it replaces, the less likely the change will disrupt protein structure and function
CONTINUED......
[Show More]


.png)