eBook PDF for Paramedic Pocketbook of Prescription Medications 1st Edition By Rose Matheson
$ 25
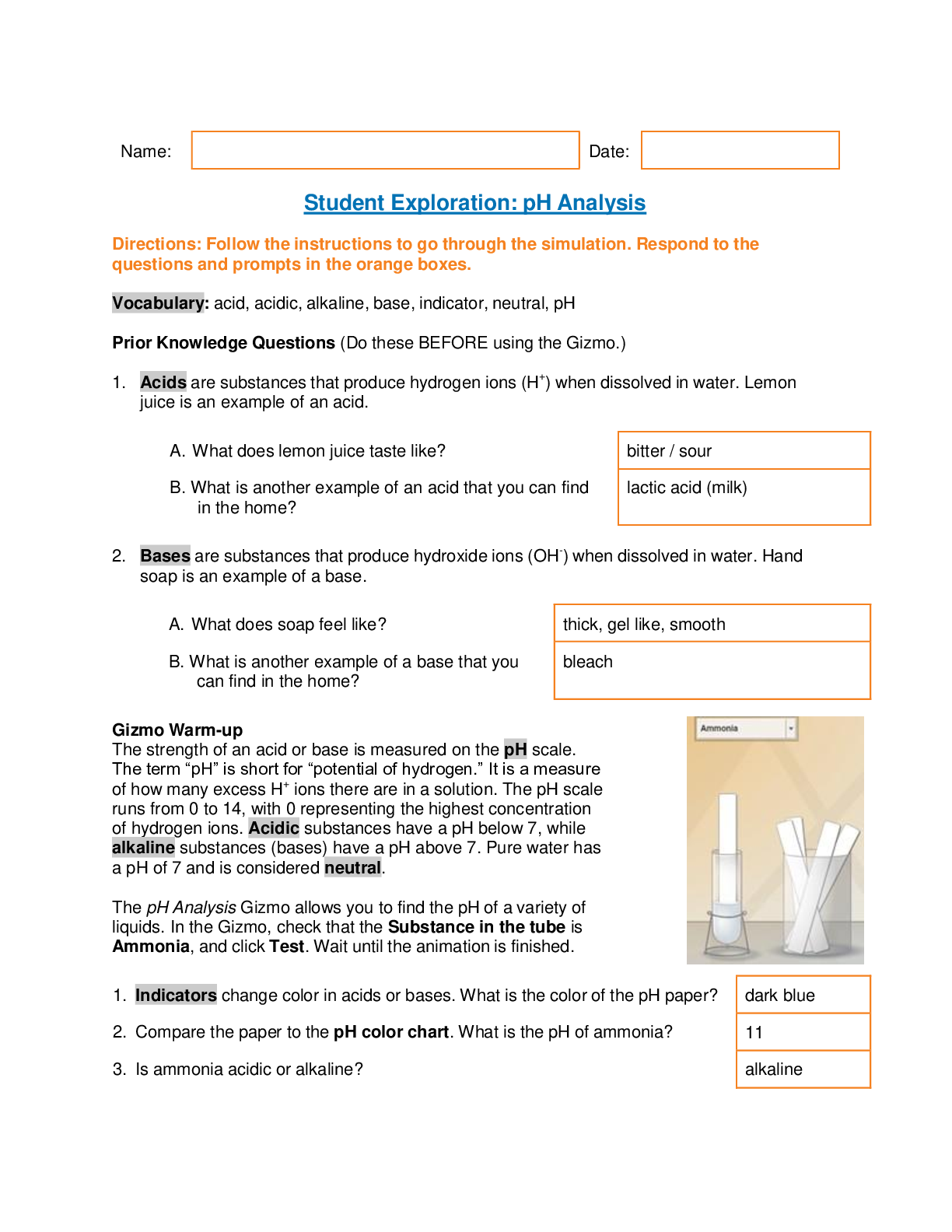
pH Analysis Questions and Answers
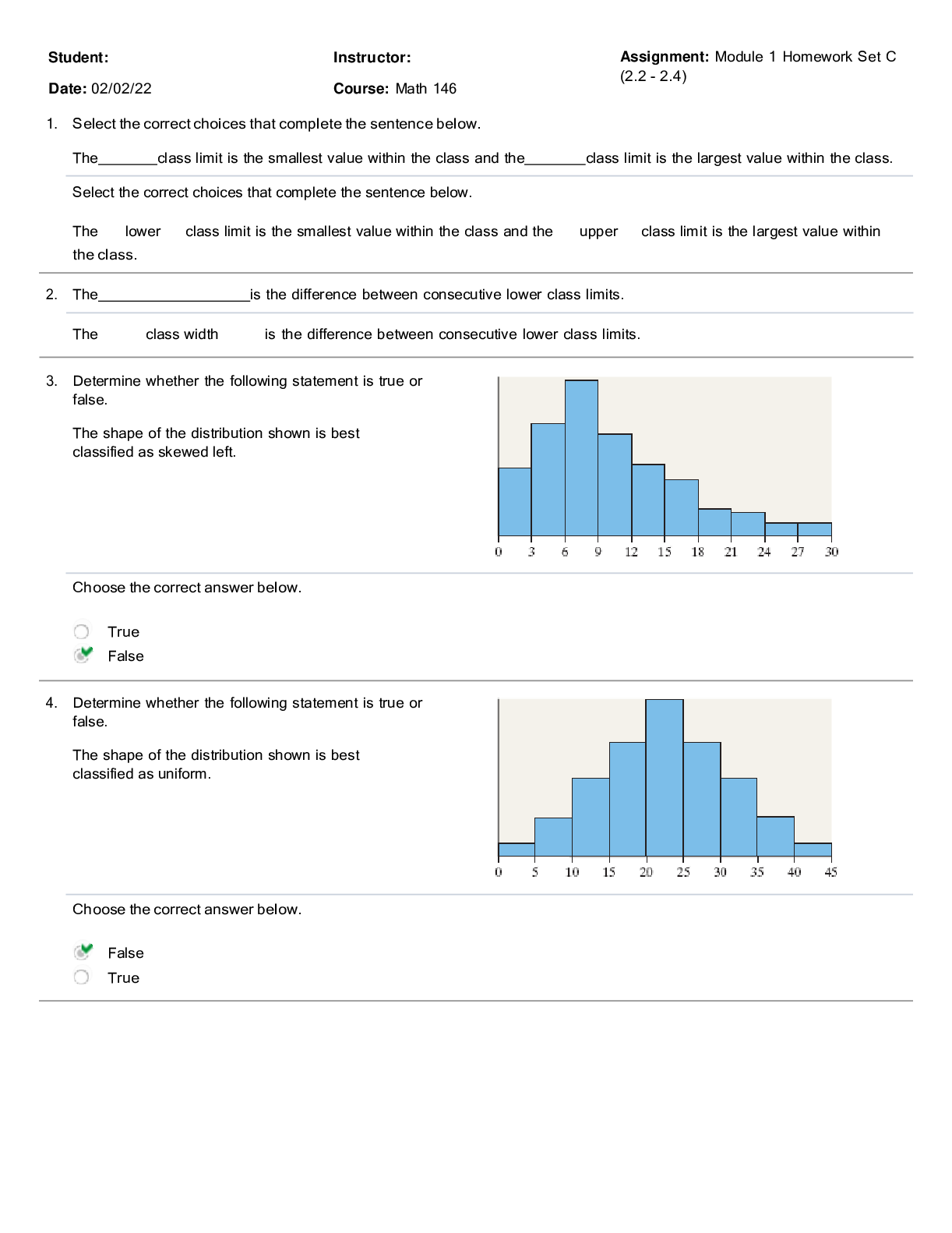
$ 7

MA278 / BSC2346 Section 06 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Final Exam, attempt Score: 59 Out of 60.
$ 20

eBook Robotic Surgery for Renal Cancer 1st Edition By Sanchia S. Goonewardene , Raj Persad ,David Albala
$ 25

Solutions Manual For Essentials of Econometrics, 5th Edition By Damodar Gujarati, Dawn Porter
$ 30

A Level Ancient History_H407/12 Mark Scheme Oct 2021 | Athens and the Greek world
$ 7
.png)
WGU C207 Data Driven Decision Making Module 2 Latest 2023 Rated A
$ 10
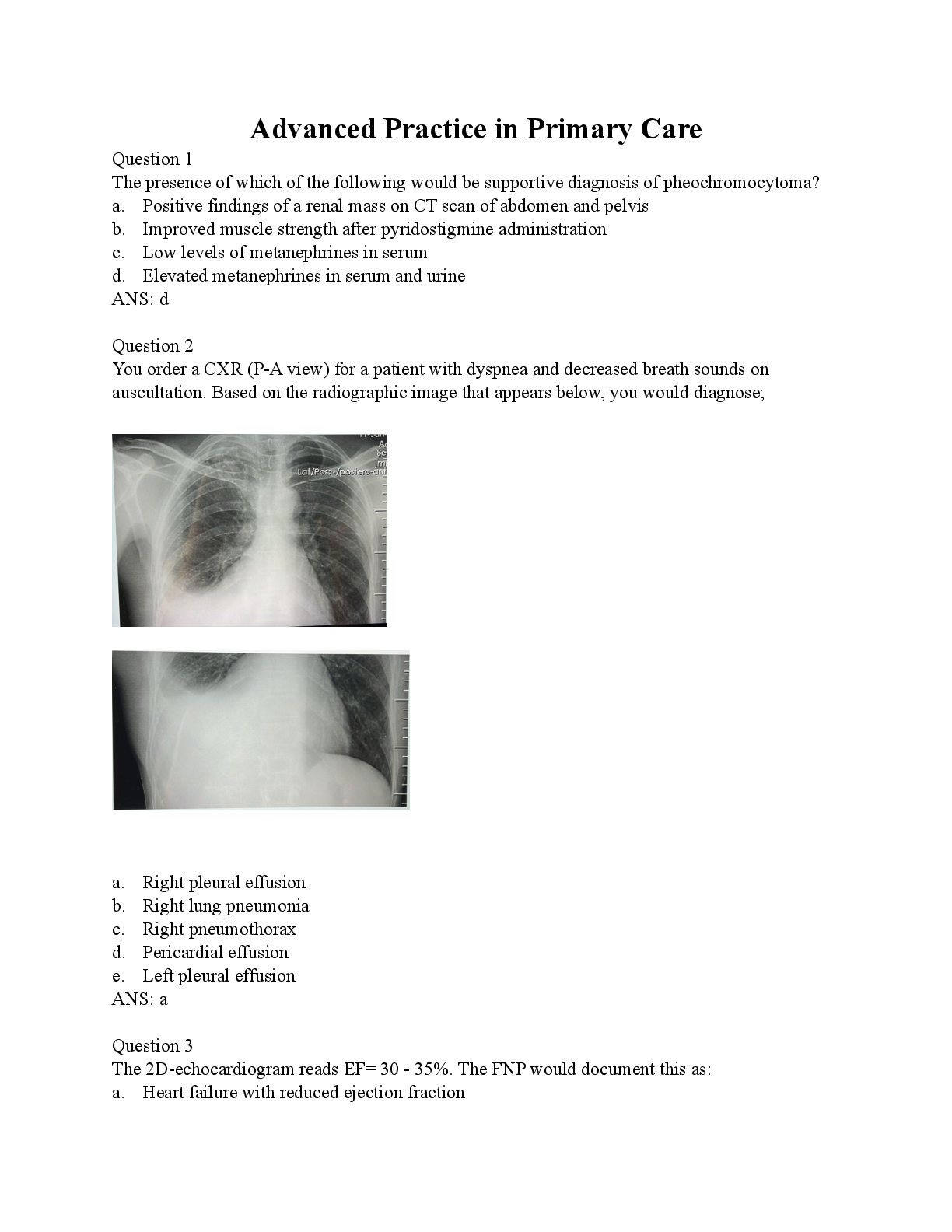
Miami Regional University: Advanced Practice in Primary Care Exam Questions with Answers 2025
$ 41

Edexcel A Level In GCE Physics (9PH0/01)Paper 1: physics I + mark scheme May 2025
$ 10

Sophia Final Milestone,100% CORRECT
$ 15

eBook PDF Child Development An Introduction 15th Edition By John Santrock, Kirby Deater-Deckard, Jennifer Lansford
$ 30

WGU Project Management C722 Unit 8 Questions and answers, graded A+. A quality audit should______________.
$ 9

Test Bank for Foundations of Earth Science, 8e Frederick Lutgens, Edward Tarbuck, Dennis Tasa (All Chapters)
$ 7.5

eBook (EPUB) [PDF] Introduction to Teaching 4th Edition By Gene Erwin Hall, Linda Quinn, Donna Gollnick
$ 30

University of the West Indies at St. Augustine - BIOC 2169BIOC2169-DNA Lab 2020 -STUDENT LAB-1 (1).
$ 7

Florida Civic Literacy Exam (FCLE) Practice Exam - Q & A
$ 12

NCLEX-RN EXAM PREP 2023/2024 | 75 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS
$ 15

CJ 215 CRIMINAL JUSTICE (CRISIS INERVENTION) LATEST REVIEW FINAL EXAM Q & A 2024
$ 13
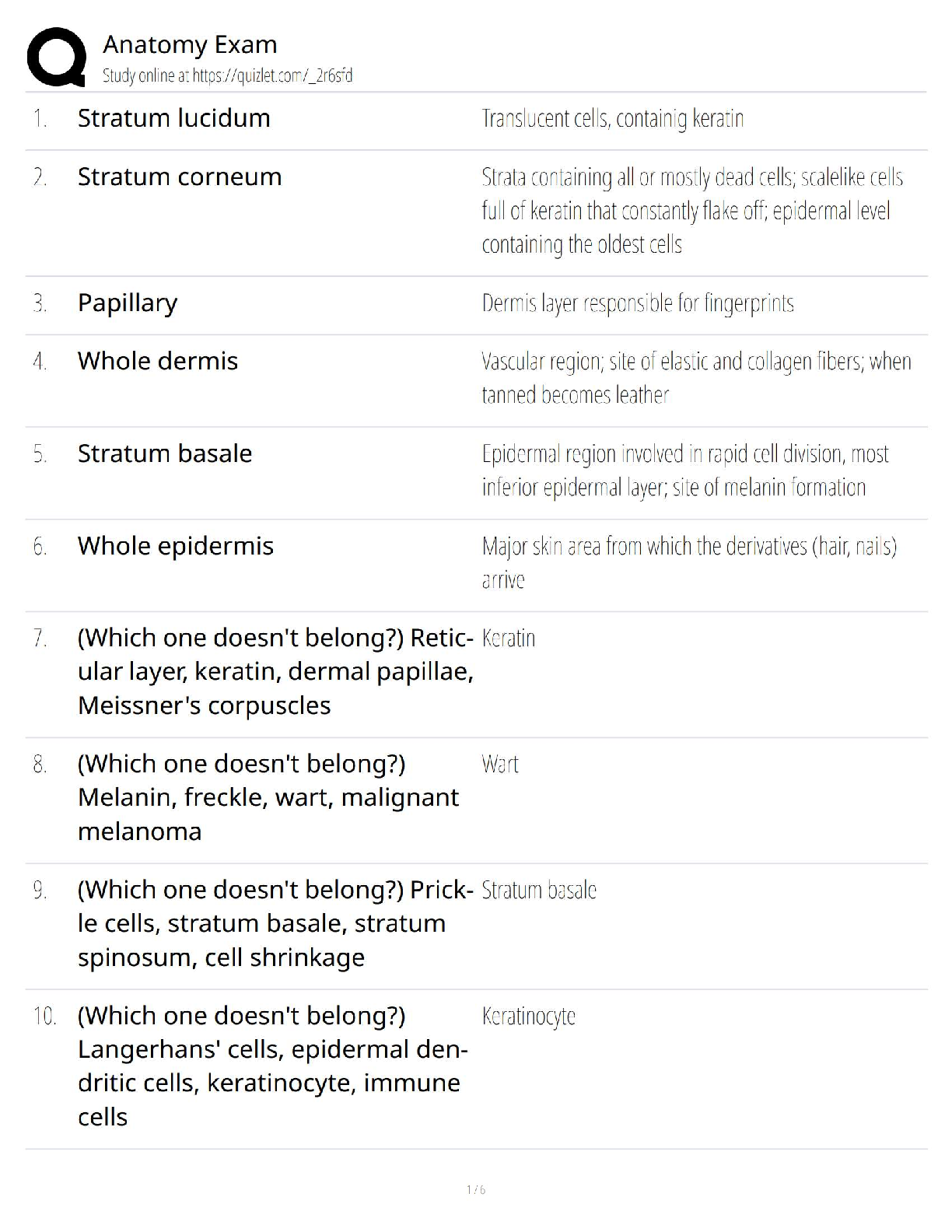
Anatomy Exam / Score 100% / 2025 Update / Test Bank, Study Notes & Practice Questions
$ 8.5
[eBook] [PDF] Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis An Agonizing Skeletal Triad By Puneetpal Singh
$ 27

Salesforce Admin 201 Practice Exam Questions with Complete Solutions
$ 15

WISCONSIN_CIVICS_EXAM_QUESTIONS_&_ANSWERS_VERIFIED_LATEST_UPDATE
$ 15

Straighterline BIO 202L Lab 18 The Reproductive System Quiz 2022 | Complete | 100% Correct Answers
$ 5

2024 DMV Nevada Permit Test New Full TEST | Questions and Answers ( Included ) 100% Correct
$ 11

MN568 Unit 2 Exam : Kaplan University (graded A) {Latest 2019 Questions & Answers}
$ 21
eBook Protein Interactions The Molecular Basis of Interactomics 1st Edition By Volkhard Helms, Olga V. Kalinina
$ 30

ATI RN Comprehensive Predictor 2019 Test With Correct And Verified Answers
$ 38.5

SOPHIA PATHWAY- MACROECONOMICS Milestone 3
$ 10

BIO 235 midterm 2 version B Study Notes 2b study notes
$ 10.5

WGU D002- Professional, Ethical, and Legal Practices for Special Education Verified Solutions 100%
$ 10.5
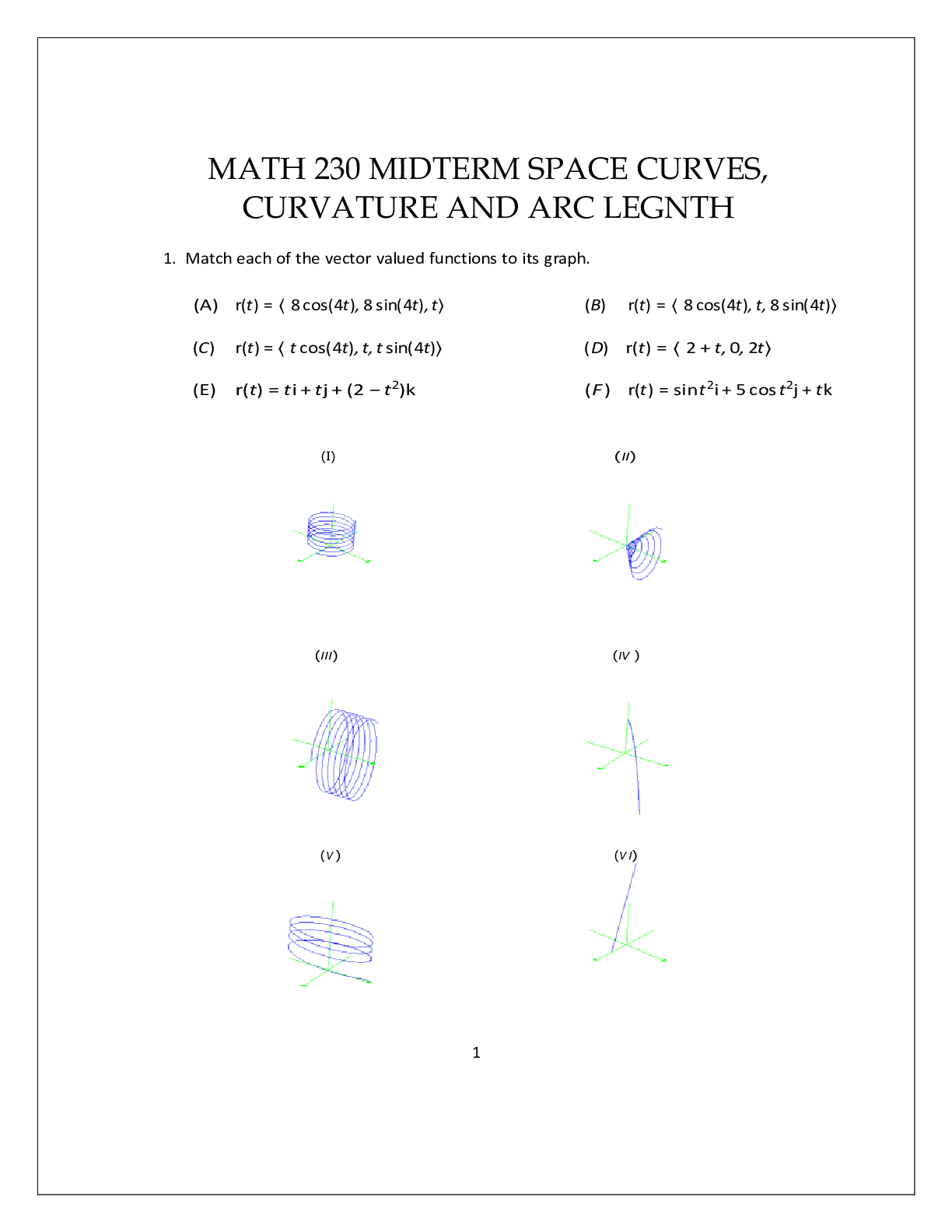
MATH 230 MIDTERM 1 SPACE CURVES, CURVATURE AND ARC LEGNTH OFFICIAL PRACTICE QUESTIONS 2024
$ 14

ECE Test Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, graded A+
$ 6

NR 503 Week 3 Discussion: Chronic Health and Occupational Health Articles
$ 10
.png)
University of PhoenixCJA 224Plea Bargaining Paper_Week 3
$ 9

SEJPME Lesson 5 Crisis Response and Limited Contingency-St John's University: Complete Solution 100% Correct
$ 15

MGT 6681 Quiz Review complete exam questions and answers solved solution










.png)

.png)